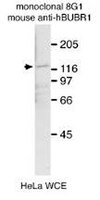
MASTL promotes cyclin B1 destruction by enforcing Cdc20-independent binding of cyclin B1 to the APC/C.
Voets, E; Wolthuis, R
Biology open
4
484-95
2015
Show Abstract
When cells enter mitosis, the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is activated by phosphorylation and binding of Cdc20. The RXXL destruction box (D-box) of cyclin B1 only binds Cdc20 after release of the spindle checkpoint in metaphase, initiating cyclin B1 ubiquitination upon chromosome bi-orientation. However, we found that cyclin B1, through Cdk1 and Cks, is targeted to the phosphorylated APC/C(Cdc20) at the start of prometaphase, when the spindle checkpoint is still active. Here, we show that MASTL is essential for cyclin B1 recruitment to the mitotic APC/C and that this occurs entirely independently of Cdc20. Importantly, MASTL-directed binding of cyclin B1 to spindle checkpoint-inhibited APC/C(Cdc20) critically supports efficient cyclin B1 destruction after checkpoint release. A high incidence of anaphase bridges observed in response to MASTL RNAi may result from cyclin B1 remaining after securin destruction, which is insufficient to keep MASTL-depleted cells in mitosis but delays the activation of separase. | 25750436
 |
Formation of stable attachments between kinetochores and microtubules depends on the B56-PP2A phosphatase.
Foley, EA; Maldonado, M; Kapoor, TM
Nature cell biology
13
1265-71
2011
Show Abstract
Error-free chromosome segregation depends on the precise regulation of phosphorylation to stabilize kinetochore-microtubule attachments (K-fibres) on sister chromatids that have attached to opposite spindle poles (bi-oriented). In many instances, phosphorylation correlates with K-fibre destabilization. Consistent with this, multiple kinases, including Aurora B and Plk1, are enriched at kinetochores of mal-oriented chromosomes when compared with bi-oriented chromosomes, which have stable attachments. Paradoxically, however, these kinases also target to prometaphase chromosomes that have not yet established spindle attachments and it is therefore unclear how kinetochore-microtubule interactions can be stabilized when kinase levels are high. Here we show that the generation of stable K-fibres depends on the B56-PP2A phosphatase, which is enriched at centromeres/kinetochores of unattached chromosomes. When B56-PP2A is depleted, K-fibres are destabilized and chromosomes fail to align at the spindle equator. Strikingly, B56-PP2A depletion increases the level of phosphorylation of Aurora B and Plk1 kinetochore substrates as well as Plk1 recruitment to kinetochores. Consistent with increased substrate phosphorylation, we find that chemical inhibition of Aurora or Plk1 restores K-fibres in B56-PP2A-depleted cells. Our findings reveal that PP2A, an essential tumour suppressor, tunes the balance of phosphorylation to promote chromosome-spindle interactions during cell division. | 21874008
 |
Overexpression of the dynein light chain km23-1 in human ovarian carcinoma cells inhibits tumor formation in vivo and causes mitotic delay at prometaphase/metaphase.
Pulipati, Nageswara R, et al.
Int. J. Cancer, 129: 553-64 (2011)
2011
Show Abstract
km23-1 is a dynein light chain that was identified as a TGFβ receptor-interacting protein. To investigate whether km23-1 controls human ovarian carcinoma cell (HOCC) growth, we established a tet-off inducible expression system in SKOV-3 cells in which the expression of km23-1 is induced upon doxycycline removal. We found that forced expression of km23-1 inhibited both anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent growth of SKOV-3 cells. More importantly, induction of km23-1 expression substantially reduced the tumorigenicity of SKOV-3 cells in a xenograft model in vivo. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of SKOV-3 and IGROV-1 HOCCs demonstrated that the cells were accumulating at G2/M. Phospho-MEK, phospho-ERK and cyclin B1 were elevated, as was the mitotic index, suggesting that km23-1 suppresses HOCCs growth by inducing a mitotic delay. Immunofluorescence analyses demonstrated that the cells were accumulating at prometaphase/metaphase with increases in multipolar and multinucleated cells. Further, although the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein BubR1 was present at the prometaphase kinetochore in Dox+/- cells, it was inappropriately retained at the metaphase kinetochore in Dox- cells. Thus, the mechanism by which high levels of km23-1 suppress ovarian carcinoma growth in vitro and inhibit ovary tumor formation in vivo appears to involve a BubR1-related mitotic delay. | 21469138
 |
Heat shock protein inhibitors, 17-DMAG and KNK437, enhance arsenic trioxide-induced mitotic apoptosis.
Yi-Chen Wu,Wen-Yen Yen,Te-Chang Lee,Ling-Huei Yih
Toxicology and applied pharmacology
236
2009
Show Abstract
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) has recently emerged as a promising therapeutic agent in leukemia because of its ability to induce apoptosis. However, there is no sufficient evidence to support its therapeutic use for other types of cancers. In this study, we investigated if, and how, 17-dimethylaminoethylamino-17-demethoxy-geldanamycin (17-DMAG), an antagonist of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90), and KNK437, a HSP synthesis inhibitor, potentiated the cytotoxic effect of ATO. Our results showed that cotreatment with ATO and either 17-DMAG or KNK437 significantly increased ATO-induced cell death and apoptosis. siRNA-mediated attenuation of the expression of the inducible isoform of HSP70 (HSP70i) or HSP90alpha/beta also enhanced ATO-induced apoptosis. In addition, cotreatment with ATO and 17-DMAG or KNK437 significantly increased ATO-induced mitotic arrest and ATO-induced BUBR1 phosphorylation and PDS1 accumulation. Cotreatment also significantly increased the percentage of mitotic cells with abnormal mitotic spindles and promoted metaphase arrest as compared to ATO treatment alone. These results indicated that 17-DMAG or KNK437 may enhance ATO cytotoxicity by potentiating mitotic arrest and mitotic apoptosis possibly through increased activation of the spindle checkpoint. | 19371599
 |
Subcellular localization of the spindle proteins Aurora A, Mad2, and BUBR1 assessed by immunohistochemistry.
Burum-Auensen, E; De Angelis, PM; Schjølberg, AR; Kravik, KL; Aure, M; Clausen, OP
The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society
55
477-86
2007
Show Abstract
The spindle checkpoint, the primary mechanism to ensure that two daughter cells receive the same amount of DNA, is compromised in many malignant tumors and has been implicated as a contributor to aneuploidy and carcinogenesis. The extent of expression and subcellular localization of the spindle proteins Aurora A, Mad2, and BUBR1 varies considerably in different immunohistochemical (IHC) reports from archival tumor tissues. Given the conflicting reports in the literature about the localization of these proteins, we examined the subcellular localization of Aurora kinase A, Mad2, and BUBR1 in normal and cancerous human tissues by IHC. In normal tissues, Aurora A was mainly localized to the nucleus when monoclonal or purified polyclonal antibodies were used, and Mad2 was localized to the nucleus, whereas BUBR1 was localized to the cytoplasm. In malignant tissues, Aurora A showed additional staining in the cytoplasm in the majority of tumors analyzed. Furthermore, BUBR1 was also localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm in a significant fraction of tumors. Subcellular localization of Mad2 was similar in normal and malignant tissues. Thus, the validity of some earlier IHC studies of Aurora A, Mad2, and BUBR1 should be reconsidered, indicating that high-quality antibodies and a high-alkaline antigen-retrieval technique are required to achieve optimal results. We conclude that the subcellular localizations of these spindle proteins are different, although they have overlapping biological functions, and that Aurora A and BUBR1 undergo a shift in the subcellular localization during malignant transformation. | 17242465
 |