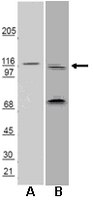
Clathrin light chains are required for the gyrating-clathrin recycling pathway and thereby promote cell migration.
Majeed, SR; Vasudevan, L; Chen, CY; Luo, Y; Torres, JA; Evans, TM; Sharkey, A; Foraker, AB; Wong, NM; Esk, C; Freeman, TA; Moffett, A; Keen, JH; Brodsky, FM
Nature communications
5
3891
2014
Show Abstract
The clathrin light chain (CLC) subunits participate in several membrane traffic pathways involving both clathrin and actin, through binding the actin-organizing huntingtin-interacting proteins (Hip). However, CLCs are dispensable for clathrin-mediated endocytosis of many cargoes. Here we observe that CLC depletion affects cell migration through Hip binding and reduces surface expression of β1-integrin by interference with recycling following normal endocytosis of inactive β1-integrin. CLC depletion and expression of a modified CLC also inhibit the appearance of gyrating (G)-clathrin structures, known mediators of rapid recycling of transferrin receptor from endosomes. Expression of the modified CLC reduces β1-integrin and transferrin receptor recycling, as well as cell migration, implicating G-clathrin in these processes. Supporting a physiological role for CLC in migration, the CLCb isoform of CLC is upregulated in migratory human trophoblast cells during uterine invasion. Together, these studies establish CLCs as mediating clathrin-actin interactions needed for recycling by G-clathrin during migration. | Immunofluorescence | 24852344
 |