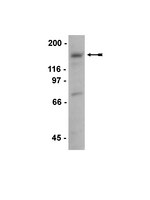
CFEOM1-Associated Kinesin KIF21A Is a Cortical Microtubule Growth Inhibitor.
van der Vaart, Babet, et al.
Dev. Cell, (2013)
2013
Show Abstract
Mechanisms controlling microtubule dynamics at the cell cortex play a crucial role in cell morphogenesis and neuronal development. Here, we identified kinesin-4 KIF21A as an inhibitor of microtubule growth at the cell cortex. In vitro, KIF21A suppresses microtubule growth and inhibits catastrophes. In cells, KIF21A restricts microtubule growth and participates in organizing microtubule arrays at the cell edge. KIF21A is recruited to the cortex by KANK1, which coclusters with liprin-α1/β1 and the components of the LL5β-containing cortical microtubule attachment complexes. Mutations in KIF21A have been linked to congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles type 1 (CFEOM1), a dominant disorder associated with neurodevelopmental defects. CFEOM1-associated mutations relieve autoinhibition of the KIF21A motor, and this results in enhanced KIF21A accumulation in axonal growth cones, aberrant axon morphology, and reduced responsiveness to inhibitory cues. Our study provides mechanistic insight into cortical microtubule regulation and suggests that altered microtubule dynamics contribute to CFEOM1 pathogenesis. | 24120883
 |
KIF1Bbeta2, capable of interacting with CHP, is localized to synaptic vesicles.
Nakamura, Norihiro, et al.
J. Biochem., 132: 483-91 (2002)
2002
Show Abstract
Kinesin family proteins are microtubule-dependent molecular motors involved in the intracellular motile process. Using a Ca2+ -binding protein, CHP (calcineurin B homologous protein), as a bait for yeast two hybrid screening, we identified a novel kinesin-related protein, KIF1Bbeta2. KIF1Bbeta2 is a member of the KIF1 subfamily of kinesin-related proteins, and consists of an amino terminal KIF1B-type motor domain followed by a tail region highly similar to that of KIF1A. CHP binds to regions adjacent to the motor domains of KIF1Bbeta2 and KIF1B, but not to those of the other KIF1 family members, KIF1A and KIF1C. Immunostaining of neuronal cells showed that a significant portion of KIF1Bbeta2 is co-localized with synaptophysin, a marker protein for synaptic vesicles, but not with a mitochondria-staining dye. Subcellular fractionation analysis indicated the co-localization of KIF1Bbeta2 with synaptophysin. These results suggest that KIF1Bbeta2, a novel CHP-interacting molecular motor, mediates the transport of synaptic vesicles in neuronal cells. | 12204119
 |
Novel dendritic kinesin sorting identified by different process targeting of two related kinesins: KIF21A and KIF21B.
Marszalek, J R, et al.
J. Cell Biol., 145: 469-79 (1999)
1999
Show Abstract
Neurons use kinesin and dynein microtubule-dependent motor proteins to transport essential cellular components along axonal and dendritic microtubules. In a search for new kinesin-like proteins, we identified two neuronally enriched mouse kinesins that provide insight into a unique intracellular kinesin targeting mechanism in neurons. KIF21A and KIF21B share colinear amino acid similarity to each other, but not to any previously identified kinesins outside of the motor domain. Each protein also contains a domain of seven WD-40 repeats, which may be involved in binding to cargoes. Despite the amino acid sequence similarity between KIF21A and KIF21B, these proteins localize differently to dendrites and axons. KIF21A protein is localized throughout neurons, while KIF21B protein is highly enriched in dendrites. The plus end-directed motor activity of KIF21B and its enrichment in dendrites indicate that models suggesting that minus end-directed motor activity is sufficient for dendrite specific motor localization are inadequate. We suggest that a novel kinesin sorting mechanism is used by neurons to localize KIF21B protein to dendrites since its mRNA is restricted to the cell body. | 10225949
 |