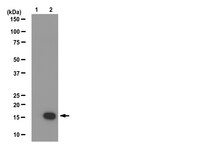
Using the avian mutant talpid2 as a disease model for understanding the oral-facial phenotypes of oral-facial-digital syndrome.
Schock, EN; Chang, CF; Struve, JN; Chang, YT; Chang, J; Delany, ME; Brugmann, SA
Disease models & mechanisms
8
855-66
2015
Show Abstract
Oral-facial-digital syndrome (OFD) is a ciliopathy that is characterized by oral-facial abnormalities, including cleft lip and/or palate, broad nasal root, dental anomalies, micrognathia and glossal defects. In addition, these individuals have several other characteristic abnormalities that are typical of a ciliopathy, including polysyndactyly, polycystic kidneys and hypoplasia of the cerebellum. Recently, a subset of OFD cases in humans has been linked to mutations in the centriolar protein C2 Ca(2+)-dependent domain-containing 3 (C2CD3). Our previous work identified mutations in C2CD3 as the causal genetic lesion for the avian talpid(2) mutant. Based on this common genetic etiology, we re-examined the talpid(2) mutant biochemically and phenotypically for characteristics of OFD. We found that, as in OFD-affected individuals, protein-protein interactions between C2CD3 and oral-facial-digital syndrome 1 protein (OFD1) are reduced in talpid(2) cells. Furthermore, we found that all common phenotypes were conserved between OFD-affected individuals and avian talpid(2) mutants. In light of these findings, we utilized the talpid(2) model to examine the cellular basis for the oral-facial phenotypes present in OFD. Specifically, we examined the development and differentiation of cranial neural crest cells (CNCCs) when C2CD3-dependent ciliogenesis was impaired. Our studies suggest that although disruptions of C2CD3-dependent ciliogenesis do not affect CNCC specification or proliferation, CNCC migration and differentiation are disrupted. Loss of C2CD3-dependent ciliogenesis affects the dispersion and directional persistence of migratory CNCCs. Furthermore, loss of C2CD3-dependent ciliogenesis results in dysmorphic and enlarged CNCC-derived facial cartilages. Thus, these findings suggest that aberrant CNCC migration and differentiation could contribute to the pathology of oral-facial defects in OFD. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 26044959
 |
Salinomycin induces apoptosis and senescence in breast cancer: upregulation of p21, downregulation of survivin and histone H3 and H4 hyperacetylation.
Al Dhaheri, Y; Attoub, S; Arafat, K; Abuqamar, S; Eid, A; Al Faresi, N; Iratni, R
Biochimica et biophysica acta
3121-35
2013
Show Abstract
In the present study, we investigated the effect of Salinomycin on the survival of three human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, T47D and MDA-MB-231 grown in adherent culture conditions.Cell viability was measured by Cell Titer-Glo and Trypan blue exclusion assay. Apoptosis was determined by caspase 3/7 activation, PARP cleavage and Annexin V staining. Cell cycle distribution was assessed by propidium iodide flow cytometry. Senescence was confirmed by measuring the senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity. Changes in protein expression and histone hyperacetylation was determined by western blot and confirmed by immunofluorescence assay.Salinomycin was able to inhibit the growth of the three cell lines in time- and concentration-dependent manners. We showed that depending on the concentrations used, Salinomycin elicits different effects on the MDA-MB-231 cells. High concentrations of Salinomycin induced a G2 arrest, downregulation of survivin and triggered apoptosis. Interestingly, treatment with low concentrations of Salinomycin induced a transient G1 arrest at earlier time point and G2 arrest at later point and senescence associated with enlarged cellmorphology, upregulation of p21 protein, increase in histone H3 and H4 hyperacetylation and expression of SA-β-Gal activity. Furthermore, we found that Salinomycin was able to potentiate the killing of the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells, by the chemotherapeutic agents, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen and frondo side A, respectively.Our data are the first to link senescence and histone modifications to Salinomycin.This study provides a new insight to better understand the mechanism of action of Salinomycin, at least in breast cancer cells. | Immunofluorescence | 23352703
 |
Mitotic arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer cells induced by Origanum majorana extract: upregulation of TNF-α and downregulation of survivin and mutant p53.
Al Dhaheri, Y; Eid, A; AbuQamar, S; Attoub, S; Khasawneh, M; Aiche, G; Hisaindee, S; Iratni, R
PloS one
8
e56649
2013
Show Abstract
In the present study, we investigated the effect of Origanum majorana ethanolic extract on the survival of the highly proliferative and invasive triple-negative p53 mutant breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231.We found that O. majorana extract (OME) was able to inhibit the viability of the MDA-MB-231 cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. The effect of OME on cellular viability was further confirmed by the inhibition of colony growth. We showed, depending on the concentration used, that OME elicited different effects on the MDA-MB 231 cells. Concentrations of 150 and 300 µg/mL induced an accumulation of apoptotic-resistant population of cells arrested in mitotis and overexpressing the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21 and the inhibitor of apoptosis, survivin. On the other hand, higher concentrations of OME (450 and 600 µg/mL) triggered a massive apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway, including the activation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), caspase 8, caspase 3, and cleavage of PARP, downregulation of survivin as well as depletion of the mutant p53 in MDA-MB-231 cells. Furthermore, OME induced an upregulation of γ-H2AX, a marker of double strand DNA breaks and an overall histone H3 and H4 hyperacetylation.Our findings provide strong evidence that O. majorana may be a promising chemopreventive and therapeutic candidate against cancer especially for highly invasive triple negative p53 mutant breast cancer; thus validating its complementary and alternative medicinal use. | Immunohistochemistry | 23451065
 |
Phosphorylation-enabled binding of SGO1-PP2A to cohesin protects sororin and centromeric cohesion during mitosis.
Liu, H; Rankin, S; Yu, H
Nature cell biology
15
40-9
2013
Show Abstract
Timely dissolution of sister-chromatid cohesion in mitosis ensures accurate chromosome segregation to guard against aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. The complex of shugoshin and protein phosphatase 2A (SGO1-PP2A) protects cohesin at centromeres from premature removal by mitotic kinases and WAPL in prophase. Here we address the regulation and mechanism of human SGO1 in centromeric cohesion protection, and show that cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-mediated, mitosis-specific phosphorylation of SGO1 activates its cohesion-protection function and enables its direct binding to cohesin. The phospho-SGO1-bound cohesin complex contains PP2A, PDS5 and hypophosphorylated sororin, but lacks WAPL. Expression of non-phosphorylatable sororin bypasses the requirement for SGO1-PP2A in centromeric cohesion. Thus, mitotic phosphorylation of SGO1 targets SGO1-PP2A to cohesin, promotes dephosphorylation of PDS5-bound sororin and protects centromeric cohesin from WAPL. PP2A-orchestrated, site-selective dephosphorylation of cohesin and its regulators underlies centromeric cohesion protection. | Immunoblotting (Western), Immunohistochemistry | 23242214
 |
Production of viable gametes without meiosis in maize deficient for an ARGONAUTE protein.
Singh, M; Goel, S; Meeley, RB; Dantec, C; Parrinello, H; Michaud, C; Leblanc, O; Grimanelli, D
The Plant cell
23
443-58
2011
Show Abstract
Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction through seeds in angiosperms. Apomictic plants bypass meiosis and fertilization, developing offspring that are genetically identical to their mother. In a genetic screen for maize (Zea mays) mutants mimicking aspects of apomixis, we identified a dominant mutation resulting in the formation of functional unreduced gametes. The mutant shows defects in chromatin condensation during meiosis and subsequent failure to segregate chromosomes. The mutated locus codes for AGO104, a member of the ARGONAUTE family of proteins. AGO104 accumulates specifically in somatic cells surrounding the female meiocyte, suggesting a mobile signal rather than cell-autonomous control. AGO104 is necessary for non-CG methylation of centromeric and knob-repeat DNA. Digital gene expression tag profiling experiments using high-throughput sequencing show that AGO104 influences the transcription of many targets in the ovaries, with a strong effect on centromeric repeats. AGO104 is related to Arabidopsis thaliana AGO9, but while AGO9 acts to repress germ cell fate in somatic tissues, AGO104 acts to repress somatic fate in germ cells. Our findings show that female germ cell development in maize is dependent upon conserved small RNA pathways acting non-cell-autonomously in the ovule. Interfering with this repression leads to apomixis-like phenotypes in maize. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 21325139
 |