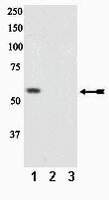
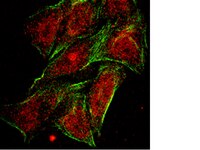
Loss of NDRG2 expression activates PI3K-AKT signalling via PTEN phosphorylation in ATLL and other cancers.
Nakahata, S; Ichikawa, T; Maneesaay, P; Saito, Y; Nagai, K; Tamura, T; Manachai, N; Yamakawa, N; Hamasaki, M; Kitabayashi, I; Arai, Y; Kanai, Y; Taki, T; Abe, T; Kiyonari, H; Shimoda, K; Ohshima, K; Horii, A; Shima, H; Taniwaki, M; Yamaguchi, R; Morishita, K
Nature communications
5
3393
2014
Show Abstract
Constitutive phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT activation has a causal role in adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma (ATLL) and other cancers. ATLL cells do not harbour genetic alterations in PTEN and PI3KCA but express high levels of PTEN that is highly phosphorylated at its C-terminal tail. Here we report a mechanism for the N-myc downstream-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2)-dependent regulation of PTEN phosphatase activity via the dephosphorylation of PTEN at the Ser380, Thr382 and Thr383 cluster within the C-terminal tail. We show that NDRG2 is a PTEN-binding protein that recruits protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) to PTEN. The expression of NDRG2 is frequently downregulated in ATLL, resulting in enhanced phosphorylation of PTEN at the Ser380/Thr382/Thr383 cluster and enhanced activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway. Given the high incidence of T-cell lymphoma and other cancers in NDRG2-deficient mice, PI3K-AKT activation via enhanced PTEN phosphorylation may be critical for the development of cancer. | 24569712
 |
Olfactory deficits in Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) disease.
Hovakimyan, M; Meyer, A; Lukas, J; Luo, J; Gudziol, V; Hummel, T; Rolfs, A; Wree, A; Witt, M
PloS one
8
e82216
2013
Show Abstract
Niemann-Pick type C disease (NPC) is a rare autosomal recessive lipid storage disease characterized by progressive neurodegeneration. As only a few studies have been conducted on the impact of NPC on sensory systems, we used a mutant mouse model (NPC1(-/-)) to examine the effects of this disorder to morphologically distinct regions of the olfactory system, namely the olfactory epithelium (OE) and olfactory bulb (OB).For structural and functional analysis immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy, western blotting, and electrophysiology have been applied. For histochemistry and western blotting, we used antibodies against a series of neuronal and glia marker proteins, as well as macrophage markers. NPC1(-/-) animals present myelin-like lysosomal deposits in virtually all types of cells of the peripheral and central olfactory system. Especially supporting cells of the OE and central glia cells are affected, resulting in pronounced astrocytosis and microgliosis in the OB and other olfactory cortices. Up-regulation of Galectin-3, Cathepsin D and GFAP in the cortical layers of the OB underlines the critical role and location of the OB as a possible entrance gate for noxious substances. Unmyelinated olfactory afferents of the lamina propria seem less affected than ensheathing cells. Supporting the structural findings, electro-olfactometry of the olfactory mucosa suggests that NPC1(-/-) animals exhibit olfactory and trigeminal deficits.Our data demonstrate a pronounced neurodegeneration and glia activation in the olfactory system of NPC1(-/-), which is accompanied by sensory deficits. | 24391715
 |
Compensatory effects in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling network following receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition.
Alexey Goltsov,Dana Faratian,Simon P Langdon,James Bown,Igor Goryanin,David J Harrison
Cellular signalling
23
2011
Show Abstract
Overcoming de novo and acquired resistance to anticancer drugs that target signaling networks is a formidable challenge for drug design and effective cancer therapy. Understanding the mechanisms by which this resistance arises may offer a route to addressing the insensitivity of signaling networks to drug intervention and restore the efficacy of anticancer therapy. Extending our recent work identifying PTEN as a key regulator of Herceptin sensitivity, we present an integrated theoretical and experimental approach to study the compensatory mechanisms within the PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling network that afford resistance to receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibition by anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies. In a computational model representing the dynamics of the signaling network, we define a single control parameter that encapsulates the balance of activities of the enzymes involved in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT cycle. By varying this control parameter we are able to demonstrate both distinct dynamic regimes of behavior of the signaling network and the transitions between those regimes. We demonstrate resistance, sensitivity, and suppression of RTK signals by the signaling network. Through model analysis we link the sensitivity-to-resistance transition to specific compensatory mechanisms within the signaling network. We study this transition in detail theoretically by variation of activities of PTEN, PI3K, AKT enzymes, and use the results to inform experiments that perturb the signaling network using combinatorial inhibition of RTK, PTEN, and PI3K enzymes in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. We find good alignment between theoretical predictions and experimental results. We discuss the application of the results to the challenges of hypersensitivity of the signaling network to RTK signals, suppression of drug resistance, and efficacy of drug combinations in anticancer therapy. | 20951800
 |