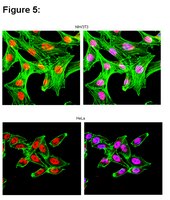
RNA-binding proteins regulate the expression of the immune activating ligand MICB.
Nachmani, D; Gutschner, T; Reches, A; Diederichs, S; Mandelboim, O
Nature communications
5
4186
2014
Show Abstract
The recognition of stress-induced ligands by the activating receptor NKG2D expressed on cytotoxic lymphocytes is crucial for the prevention and containment of various diseases and is also one of the best-studied examples of how danger is sensed by the immune system. Still, however, the mechanisms leading to the expression of the NKG2D ligands are far from being completely understood. Here, we use an unbiased and systematic RNA pull-down approach combined with mass spectrometry to identify six RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) that bind and regulate the expression of MICB, one of the major stress-induced ligands of NKG2D. We further demonstrate that at least two of the identified RBPs function during genotoxic stress. Our data provide insights into stress recognition and hopefully open new therapeutic venues. | Western Blotting | 24924487
 |
Heat resistance of Bacillus spores when adhered to stainless steel and its relationship to spore hydrophobicity.
P Simmonds,B L Mossel,T Intaraphan,H C Deeth
Journal of food protection
66
2003
Show Abstract
Twenty-one strains of Bacillus (10 B. stearothermophilus, 3 B. cereus, and 8 B. licheniformis strains) were assayed for spore surface hydrophobicity on the basis of three measures: contact angle measurement (CAM), microbial adhesion to hydrocarbons (MATH), and hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC). On the basis of the spore surface characteristics obtained from these assays, along with data on the heat resistance of these spores in water, eight strains of Bacillus (three B. stearothermophilus, three B. cereus, and two B. licheniformis strains) either suspended in water or adhering to stainless steel were exposed to sublethal heat treatments at 90 to 110 degrees C to determine heat resistance (D-value). Significant increases in heat resistance (ranging from 3 to 400%) were observed for the eight strains adhering to stainless steel. No significant correlation was found between these heat resistance increases and spore surface characteristics as determined by the three hydrophobicity assays. There was a significant positive correlation between the hydrophobicity data obtained by the MATH assay and those obtained by the HIC assay, but these data did not correlate with those obtained by the CAM assay. | | 14627285
 |