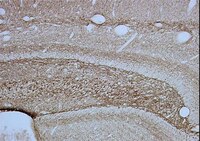
Multipotent neural crest stem cell-like cells from rat vibrissa dermal papilla induce neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells.
Li, M; Liu, JY; Wang, S; Xu, H; Cui, L; Lv, S; Xu, J; Liu, S; Chi, G; Li, Y
BioMed research international
2014
186239
2014
Show Abstract
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) transplants have been approved for treating central nervous system (CNS) injuries and diseases; however, their clinical applications are limited. Here, we model the therapeutic potential of dermal papilla cells (DPCs) in vitro. DPCs were isolated from rat vibrissae and characterized by immunocytofluorescence, RT-PCR, and multidifferentiation assays. We examined whether these cells could secrete neurotrophic factors (NTFs) by using cocultures of rat pheochromocytoma cells (PC12) with conditioned medium and ELISA assay. DPCs expressed Sox10, P75, Nestin, Sox9, and differentiated into adipocytes, osteoblasts, smooth muscle cells, and neurons under specific inducing conditions. The DPC-conditioned medium (DPC-CM) induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells and promoted neurite outgrowth. Results of ELISA assay showed that compared to BMSCs, DPCs secreted more brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). Moreover, we observed that, compared with the total DPC population, sphere-forming DPCs expressed higher levels of Nestin and P75 and secreted greater amounts of GDNF. The DPCs from craniofacial hair follicle papilla may be a new and promising source for treating CNS injuries and diseases. | Immunocytochemistry | Rat | 25045659
 |
Deletion of ENTPD3 does not impair nucleotide hydrolysis in primary somatosensory neurons or spinal cord.
McCoy, E; Street, S; Taylor-Blake, B; Yi, J; Edwards, M; Wightman, M; Zylka, M
F1000Research
3
163
2014
Show Abstract
Ectonucleotidases are membrane-bound or secreted proteins that hydrolyze extracellular nucleotides. Recently, we identified three ectonucleotidases that hydrolyze extracellular adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) to adenosine in primary somatosensory neurons. Currently, it is unclear which ectonucleotidases hydrolyze ATP and ADP in these neurons. Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases (ENTPDs) comprise a class of enzymes that dephosphorylate extracellular ATP and ADP. Here, we found that ENTPD3 (also known as NTPDase3 or CD39L3) was located in nociceptive and non-nociceptive neurons of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG), in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, and in free nerve endings in the skin. To determine if ENTPD3 contributes directly to ATP and ADP hydrolysis in these tissues, we generated and characterized an Entpd3 knockout mouse. This mouse lacks ENTPD3 protein in all tissues examined, including the DRG, spinal cord, skin, and bladder. However, DRG and spinal cord tissues from Entpd3 (-/-) mice showed no reduction in histochemical staining when ATP, ADP, AMP, or UTP were used as substrates. Additionally, using fast-scan cyclic voltammetry (FSCV), adenosine production was not impaired in the dorsal spinal cord of Entpd3 (-/-) mice when the substrate ADP was applied. Further, Entpd3 (-/-) mice did not differ in nociceptive behaviors when compared to wild-type mice, although Entpd3 (-/-) mice showed a modest reduction in β-alanine-mediated itch. Taken together, our data indicate that deletion of Entpd3 does not impair ATP or ADP hydrolysis in primary somatosensory neurons or in dorsal spinal cord. Moreover, our data suggest there could be multiple ectonucleotidases that act redundantly to hydrolyze nucleotides in these regions of the nervous system. | | | 25717362
 |
SnoN facilitates axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury.
Do, JL; Bonni, A; Tuszynski, MH
PloS one
8
e71906
2013
Show Abstract
Adult CNS neurons exhibit a reduced capacity for growth compared to developing neurons, due in part to downregulation of growth-associated genes as development is completed. We tested the hypothesis that SnoN, an embryonically regulated transcription factor that specifies growth of the axonal compartment, can enhance growth in injured adult neurons. In vitro, SnoN overexpression in dissociated adult DRG neuronal cultures significantly enhanced neurite outgrowth. Moreover, TGF-β1, a negative regulator of SnoN, inhibited neurite outgrowth, and SnoN over-expression overcame this inhibition. We then examined whether SnoN influenced axonal regeneration in vivo: indeed, expression of a mutant form of SnoN resistant to degradation significantly enhanced axonal regeneration following cervical spinal cord injury, despite peri-lesional upregulation of TGF-β1. Thus, a developmental mechanism that specifies extension of the axonal compartment also promotes axonal regeneration after adult CNS injury. | | | 23936531
 |
TRPV1 receptors on unmyelinated C-fibres mediate colitis-induced sensitization of pelvic afferent nerve fibres in rats.
De Schepper, HU; De Winter, BY; Van Nassauw, L; Timmermans, JP; Herman, AG; Pelckmans, PA; De Man, JG
The Journal of physiology
586
5247-58
2008
Show Abstract
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease often suffer from gastrointestinal motility and sensitivity disorders. The aim of the current study was to investigate the role of transient receptor potential of the vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) receptors in the pathophysiology of colitis-induced pelvic afferent nerve sensitization. Trinitrobenzene sulphate (TNBS) colitis (7.5 mg, 30% ethanol) was induced in Wistar rats 72 h prior to the experiment. Single-fibre recordings were made from pelvic nerve afferents in the decentralized S1 dorsal root. Fibres responding to colorectal distension (CRD) were identified in controls and rats with TNBS colitis. The effect of the TRPV1 antagonist N-(4-tertiarybutylphenyl)-4-(3-chlorophyridin-2-yl)tetrahydropyrazine-1(2H)carboxamide (BCTC; 0.25-5 mg kg(-1)) or its vehicle (hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin) was tested on the afferent response to repetitive distensions (60 mmHg). Immunocytochemical staining of TRPV1 and NF200, a marker for A-fibre neurons, was performed in the dorsal root ganglia L6-S1. TNBS colitis significantly increased the response to colorectal distension of pelvic afferent C-fibres. BCTC did not significantly affect the C-fibre response in controls, but normalized the sensitized response in rats with colitis. TNBS colitis increased the spontaneous activity of C-fibres, an effect which was insensitive to administration of BCTC. TNBS colitis had no effect on Adelta-fibres, nor was their activity modulated by BCTC. TNBS colitis caused an immunocytochemical up-regulation of TRPV1 receptors in the cell bodies of pelvic afferent NF200 negative neurons. TRPV1 signalling mediates the colitis-induced sensitization of pelvic afferent C-fibres to CRD, while Adelta-fibres are neither sensitized by colitis nor affected by TRPV1 inhibition. Full Text Article | | | 18755744
 |
Netrin-1 is a novel myelin-associated inhibitor to axon growth.
Löw, K; Culbertson, M; Bradke, F; Tessier-Lavigne, M; Tuszynski, MH
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
28
1099-108
2008
Show Abstract
We investigated the influence of the bifunctional guidance molecule netrin-1 on axonal growth in the injured adult spinal cord. In the adult, netrin-1 is expressed on mature oligodendrocytes, cells of the central canal, and the meninges. Netrin-1 protein in white matter is selectively enriched adjacent to paranodal loops of myelin in nodes of Ranvier. The repulsion-mediating netrin-1 uncoordinated-5 (UNC5) receptors are expressed by neurons of the corticospinal and rubrospinal projections, and by intrinsic neurons of the spinal cord, both before and after spinal cord injury. Neutralization of netrin-1 in myelin prepared from adult rat spinal cord using UNC5 receptor bodies increases neurite outgrowth from UNC5-expressing spinal motor neurons in vitro. Furthermore, axon regeneration is inhibited in a netrin-1-enriched zone, devoid of other myelin-associated inhibitors, within spinal cord lesion sites in vivo. We conclude that netrin-1 is a novel oligodendrocyte-associated inhibitor that can contribute to axonal growth failure after adult spinal cord injury. | | | 18234888
 |
One year survival and significant reversal of motor deficits in parkinsonian rats transplanted with hESC derived dopaminergic neurons.
Ravindran Geeta,R L Ramnath,Harinarayana S Rao,Viswanathan Chandra
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
373
2008
Show Abstract
We report the generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) using a growth factor mediated multistep EB protocol and its therapeutic effects in vivo. Embryoid bodies (EBs) were cultured in insulin-transferrin-selenium fibronectin (ITSFn) media for the selection of neural precursor cells (NPC). The selected cells on exposure to N2 media supplemented with EGF, bFGF initially aggregated to generate spontaneous free floating neurospheres and on exposure to signaling molecules Shh and FGF-8 differentiated into dopaminergic neurons (40% TH+ cells/total neurons). The differentiated NPC expressed dopaminergic specific markers both at cellular and molecular levels. They secreted detectable levels of dopamine into the culture supernatant. The most unique feature of our protocol is the generation of free floating neurospheres which can be expanded for a longer period without losing their capability to differentiate into DA neurons. Further, transplantation of NPCs into the substantia nigra of 6-OHDA lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease elicited significant reversal of lesion induced motor deficits which was sustained upto the end of 1 year long study period. Immunohistochemical studies of the grafted area one year post transplantation revealed that transplanted hESC derived neural precursor cells survived, integrated in vivo and differentiated into dopaminergic neurons without teratoma formation. In summary, our results encourage the potential use of hESC derived dopaminergic neurons for future clinical application in Parkinson's disease. | | | 18565328
 |
Conditional NF-L transgene expression in mice for in vivo analysis of turnover and transport rate of neurofilaments.
Millecamps, S; Gowing, G; Corti, O; Mallet, J; Julien, JP
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
27
4947-56
2007
Show Abstract
We generated mice with doxycycline control of a human neurofilament light (NF-L) transgene in the context of the absence (tTA;hNF-L;NF-L(-/-)) or presence (tTA;hNF-L;NF-L(+/-)) of endogenous mouse NF-L proteins. Doxycycline treatment caused the rapid disappearance of human NF-L (hNF-L) mRNA in tTA;hNF-L mice, but the hNF-L proteins remained with a half-life of 3 weeks in the brain. In the sciatic nerve, the disappearance of hNF-L proteins after doxycycline treatment occurred in synchrony along the sciatic nerve, suggesting a proteolysis of NF proteins along the entire axon. The presence of permanent NF network in tTA;hNF-L;NF-L(+/-) mice further stabilized and extended longevity of hNF-L proteins by several months. Surprisingly, after cessation of doxycycline treatment, there was no evidence of leading front of newly synthesized hNF-L proteins migrating into sciatic nerve axons devoid of NF structures. The hNF-L proteins detected at weekly intervals reappeared and accumulated in synchrony at similar rate along nerve segments, a phenomenon consistent with a fast hNF-L transport into axons. We estimated the hNF-L transport rate to be of approximately 10 mm/d in axons devoid of NF structures based on the use of an adenovirus encoding tet-responsive transcriptional activator to transactivate the hNF-L transgene in hypoglossal motor neurons. These results provide in vivo evidence that the stationary NF network in axons is a key determinant of half-life and transport rate of NF proteins. | Western Blotting | | 17475803
 |
Normalization of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase and reversal of motor impairment in experimental parkinsonism with intravenous nonviral gene therapy and a brain-specific promoter.
Yun Zhang, Felix Schlachetzki, Yu-Feng Zhang, Ruben J Boado, William M Pardridge
Human gene therapy
15
339-50
2004
Show Abstract
The goal of this work was to normalize striatal tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) activity with intravenous nonviral TH gene therapy and at the same time eliminate ectopic TH gene expression in peripheral organs such as liver in the rat. TH-expression plasmids, containing either the SV40 promoter or the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) gene promoter, were globally delivered to the brain across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) after intravenous administration of pegylated immunoliposomes (PILs). The GFAP-TH- or SV40-TH-expression plasmids were encapsulated in the interior of 85-nm PILs, which were targeted across both the BBB and the neuronal cell membrane with a monoclonal antibody (mAb) to the transferrin receptor (TfR). Striatal TH activity was 98% depleted with the unilateral intracerebral injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. TH in the striatum ipsilateral to the lesion was normalized 3 days after the intravenous injection of 10 microg per rat of either the SV40-TH or the GFAP-TH plasmid DNA. Whereas the SV40-TH gene caused a 10-fold increase in hepatic TH activity, there was no increase in liver TH with the GFAP-TH gene. The GFAP-TH gene therapy caused an 82% reduction in apomorphine-induced rotation in the lesioned rats. Confocal microscopy using antibodies to TH, GFAP, and neuronal nuclei (NeuN) showed the GFAP-TH gene was selectively expressed in nigra-striatal neurons, with no expression in either cortical neurons, or astrocytes. These studies demonstrate that global delivery of exogenous genes to the brain is possible with intravenous nonviral gene transfer, and that ectopic gene expression is eliminated with the use of brain-specific gene promoters. | | | 15053859
 |
Staining with monoclonal antibodies to neurofilaments distinguishes between subpopulations of neurofibrillary tangles, between groups of axons and between groups of dendrites.
Kahn, J, et al.
J. Neurol., 234: 241-6 (1987)
1987
Show Abstract
A new monoclonal antibody (mab) against neurofilaments is described (mab 1215) and its reactions compared with previously characterized mabs (BF10; RT97). Mab 1215 recognizes an epitope on the heavy neurofilament polypeptide (NF-H). In Alzheimer's disease, mab 1215 recognizes only a subpopulation of neurofibrillary tangles and stains a proportion of tangles in the hippocampus but none of those in the olfactory bulb. However, mabs RT97 and BF10 stain the majority of tangles in both brain areas. Of the three antibodies, only mab BF10 recognizes, specifically, axons of granular cells in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Mab 1215 recognizes more dendrites in the pyramidal layer than either mab BF10 or mab RT97. Our observations indicate that neurofilaments are not identical in all axons and that, contrary to previous reports, NF-H is present in dendrites. The dendritic form of NF-H appears to be different from NF-H in axons and this could be due to differences in the state of phosphorylation of NF-H. We suggest that the finding that distinct subpopulations of tangles exist indicates that tangles are not static lesions. Further investigations into this possibility may illuminate the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease. | | | 3112314
 |
Alzheimer dementia and Pick's disease: neurofibrillary tangles and Pick bodies are associated with identical phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes.
Ulrich, J, et al.
Acta Neuropathol., 73: 240-6 (1987)
1987
Show Abstract
Sections of formaldehyde-fixed paraffin-embedded cortical and hippocampal brain tissue from five cases with senile dementia of Alzheimer type (SDAT) and five cases with Pick's disease (PD) were immunostained with the monoclonal antibodies (mabs) 147, RT 97, BF 10 and 8D8 with and without pretreatment with alkaline phosphatase (AP) or trypsin (Tr). The mabs 147, RT 97 and BF 10 had previously been demonstrated to bind exclusively to phosphorylated epitopes of neurofilament proteins, while mab 8D8 is shown in this report to bind mainly, but not exclusively, to phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes. The mabs RT 97, BF 10 and 8D8, but not 147 stain most, if not all, Pick bodies (PB) and Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). When sections are pretreated with AP or Tr the immunostaining with mab BF 10 is very resistent in both PB and NFT. This resistance of PB and NFT is in contrast to the reduced staining of axons and of swollen cells in PD by the same enzymatic pretreatment. Immunostaining with mab RT 97 of PB and NFT is reduced moderately by AP and considerably by Tr. Only when stained with mab 8D8 is there a discrepancy between PB and NFT in their reaction to the pretreatment with AP: NFT staining with mab 8D8 is not affected, while that of PB is abolished. Thus, in spite of their different ultrastructure, PB and NFT are very similar immunocytochemically and in the accessibility of their phosphorylated epitopes to enzymatic treatment. | | | 2441559
 |