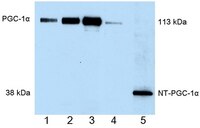
ST1202 Sigma-AldrichAnti-PGC-1α Mouse mAb (4C1.3)
This Anti-PGC-1α Mouse mAb (4C1.3) is validated for use in Immunoblotting, Immunocytochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Paraffin Sections for the detection of PGC-1α.
More>> This Anti-PGC-1α Mouse mAb (4C1.3) is validated for use in Immunoblotting, Immunocytochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Paraffin Sections for the detection of PGC-1α. Less<<Synonyms: Anti-Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor- γ Coactivator 1 α
Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Specifications Table
| Species Reactivity | Host | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|
| H, M, R | M | Monoclonal Antibody |
Pricing & Availability
| Catalog Number | Availability | Packaging | Qty/Pack | Price | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST1202-1SET |
|
Plastic ampoule | 1 set |
|
— |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Form | Liquid |
| Formulation | One vial of 100 µg antibody in 50 mM PBS, see vial for lot-specific concentration. One vial of NT-PGC-1α Positive Control, supplied as 25 µl whole cell extract in RIPA buffer containing 10 mM &beta-mercaptoethanol and 1% SDS; load 10 µl per lane; add sample buffer prior to SDS-PAGE loading. |
| Preservative | None |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information |
|---|
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalog Number | GTIN |
| ST1202-1SET | 04055977224085 |
Documentation
Anti-PGC-1α Mouse mAb (4C1.3) SDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-PGC-1α Mouse mAb (4C1.3) Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| ST1202 |
References
| Reference overview |
|---|
| Lai, L., et al. 2008. Genes Dev. 14, 1948. Rodgers, J.T., et al. 2008. FEBS Lett. 582, 46. Mazzucotelli, A., et al. 2007. Diabetes 10, 2467. Nemoto, S., et al. 2005. J. Biol. Chem. 16, 16456. |
Citations
| Title | |
|---|---|
|
| Data Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note that this data sheet is not lot-specific and is representative of the current specifications for this product. Please consult the vial label and the certificate of analysis for information on specific lots. Also note that shipping conditions may differ from storage conditions.
|