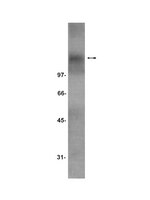
Neurotrophin receptor TrkC is an entry receptor for Trypanosoma cruzi in neural, glial, and epithelial cells.
Weinkauf, C; Salvador, R; Pereiraperrin, M
Infection and immunity
79
4081-7
2011
Show Abstract
Trypanosoma cruzi, the agent of Chagas' disease, infects a variety of mammalian cells in a process that includes multiple cycles of intracellular division and differentiation starting with host receptor recognition by a parasite ligand(s). Earlier work in our laboratory showed that the neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) receptor TrkC is activated by T. cruzi surface trans-sialidase, also known as parasite-derived neurotrophic factor (PDNF). However, it has remained unclear whether TrkC is used by T. cruzi to enter host cells. Here, we show that a neuronal cell line (PC12-NNR5) relatively resistant to T. cruzi became highly susceptible to infection when overexpressing human TrkC but not human TrkB. Furthermore, trkC transfection conferred an ∼3.0-fold intracellular growth advantage. Sialylation-deficient Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) epithelial cell lines Lec1 and Lec2 also became much more permissive to T. cruzi after transfection with the trkC gene. Additionally, NT-3 specifically blocked T. cruzi infection of the TrkC-NNR5 transfectants and of naturally permissive TrkC-bearing Schwann cells and astrocytes, as did recombinant PDNF. Two specific inhibitors of Trk autophosphorylation (K252a and AG879) and inhibitors of Trk-induced MAPK/Erk (U0126) and Akt kinase (LY294002) signaling, but not an inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, abrogated TrkC-mediated cell invasion. Antibody to TrkC blocked T. cruzi infection of the TrkC-NNR5 transfectants and of cells that naturally express TrkC. The TrkC antibody also significantly and specifically reduced cutaneous infection in a mouse model of acute Chagas' disease. TrkC is ubiquitously expressed in the peripheral and central nervous systems, and in nonneural cells infected by T. cruzi, including cardiac and gastrointestinal muscle cells. Thus, TrkC is implicated as a functional PDNF receptor in cell entry, independently of sialic acid recognition, mediating broad T. cruzi infection both in vitro and in vivo. | 21788388
 |
Overexpression of miR-128 specifically inhibits the truncated isoform of NTRK3 and upregulates BCL2 in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.
Guidi, M; Muiños-Gimeno, M; Kagerbauer, B; Martí, E; Estivill, X; Espinosa-Parrilla, Y
BMC molecular biology
11
95
2010
Show Abstract
Neurotrophins and their receptors are key molecules in the regulation of neuronal differentiation and survival. They mediate the survival of neurons during development and adulthood and are implicated in synaptic plasticity. The human neurotrophin-3 receptor gene NTRK3 yields two major isoforms, a full-length kinase-active form and a truncated non-catalytic form, which activates a specific pathway affecting membrane remodeling and cytoskeletal reorganization. The two variants present non-overlapping 3'UTRs, indicating that they might be differentially regulated at the post-transcriptional level. Here, we provide evidence that the two isoforms of NTRK3 are targeted by different sets of microRNAs, small non-coding RNAs that play an important regulatory role in the nervous system.We identify one microRNA (miR-151-3p) that represses the full-length isoform of NTRK3 and four microRNAs (miR-128, miR-485-3p, miR-765 and miR-768-5p) that repress the truncated isoform. In particular, we show that the overexpression of miR-128 - a brain enriched miRNA - causes morphological changes in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells similar to those observed using an siRNA specifically directed against truncated NTRK3, as well as a significant increase in cell number. Accordingly, transcriptome analysis of cells transfected with miR-128 revealed an alteration of the expression of genes implicated in cytoskeletal organization as well as genes involved in apoptosis, cell survival and proliferation, including the anti-apoptotic factor BCL2.Our results show that the regulation of NTRK3 by microRNAs is isoform-specific and suggest that neurotrophin-mediated processes are strongly linked to microRNA-dependent mechanisms. In addition, these findings open new perspectives for the study of the physiological role of miR-128 and its possible involvement in cell death/survival processes. Full Text Article | 21143953
 |
Support of trigeminal sensory neurons by nonneuronal p75 neurotrophin receptors.
Lixin Fan, Saulius Girnius, Bruce Oakley
Brain research. Developmental brain research
150
23-39
2004
Show Abstract
The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) binds all four mammalian neurotrophins, including neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) required for the development of select sensory neurons. This study demonstrated that many gustatory and somatosensory neurons of the tongue depend upon p75NTR. Each of thousands of filiform papillae at the front of the tongue as well as each somatosensory prominence at the back of the tongue has a small cluster of p75NTR-positive epithelial cells that is targeted by somatosensory innervation. This expression of p75NTR by epithelial target cells required NT-3 but not adult innervation. NT-3-secreting cells were adjacent to the p75NTR-positive target cells of each somatosensory organ, as demonstrated in NT-3(lacZneo) transgenic mice. In NT-3 null mutant mice, there were few lingual somatosensory neurons. In p75NTR null mutant mice, the lingual somatosensory axons were likewise absent or had deficient terminal arborizations. Cell culture indicated that substrate p75NTR can influence neuronal outgrowth. Specifically, dissociated trigeminal sensory neurons more than doubled their neurite lengths when grown on a lawn of p75NTR-overexpressing fibroblasts. This enhancement of neurite outgrowth by fibroblast p75NTR raises the possibility that epithelial target cell p75NTR may help to promote axonal arborization in vivo. The co-occurrence in p75NTR null mice of a 35% reduction in geniculate ganglion taste neurons and a shortfall of taste buds is consistent with the established role of gustatory innervation in prompting mammalian taste receptor cell differentiation. | 15126035
 |