The histone acetyltransferase MOF activates hypothalamic polysialylation to prevent diet-induced obesity in mice.
Brenachot, X; Rigault, C; Nédélec, E; Laderrière, A; Khanam, T; Gouazé, A; Chaudy, S; Lemoine, A; Datiche, F; Gascuel, J; Pénicaud, L; Benani, A
Molecular metabolism
3
619-29
2014
Show Abstract
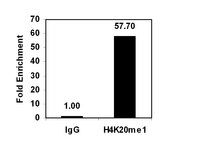
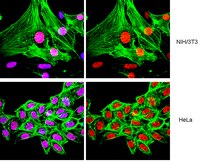
Overfeeding causes rapid synaptic remodeling in hypothalamus feeding circuits. Polysialylation of cell surface molecules is a key step in this neuronal rewiring and allows normalization of food intake. Here we examined the role of hypothalamic polysialylation in the long-term maintenance of body weight, and deciphered the molecular sequence underlying its nutritional regulation. We found that upon high fat diet (HFD), reduced hypothalamic polysialylation exacerbated the diet-induced obese phenotype in mice. Upon HFD, the histone acetyltransferase MOF was rapidly recruited on the St8sia4 polysialyltransferase-encoding gene. Mof silencing in the mediobasal hypothalamus of adult mice prevented activation of the St8sia4 gene transcription, reduced polysialylation, altered the acute homeostatic feeding response to HFD and increased the body weight gain. These findings indicate that impaired hypothalamic polysialylation contribute to the development of obesity, and establish a role for MOF in the brain control of energy balance. | 25161885
 |
LINT, a novel dL(3)mbt-containing complex, represses malignant brain tumour signature genes.
Meier, K; Mathieu, EL; Finkernagel, F; Reuter, LM; Scharfe, M; Doehlemann, G; Jarek, M; Brehm, A
PLoS genetics
8
e1002676
2012
Show Abstract
Mutations in the l(3)mbt tumour suppressor result in overproliferation of Drosophila larval brains. Recently, the derepression of different gene classes in l(3)mbt mutants was shown to be causal for transformation. However, the molecular mechanisms of dL(3)mbt-mediated gene repression are not understood. Here, we identify LINT, the major dL(3)mbt complex of Drosophila. LINT has three core subunits-dL(3)mbt, dCoREST, and dLint-1-and is expressed in cell lines, embryos, and larval brain. Using genome-wide ChIP-Seq analysis, we show that dLint-1 binds close to the TSS of tumour-relevant target genes. Depletion of the LINT core subunits results in derepression of these genes. By contrast, histone deacetylase, histone methylase, and histone demethylase activities are not required to maintain repression. Our results support a direct role of LINT in the repression of brain tumour-relevant target genes by restricting promoter access. | 22570633
 |