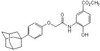
Channel-forming peptide modulates transepithelial electrical conductance and solute permeability.
Broughman, JR; Brandt, RM; Hastings, C; Iwamoto, T; Tomich, JM; Schultz, BD
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology
286
C1312-23
2004
Show Abstract
NC-1059, a synthetic channel-forming peptide, transiently increases transepithelial electrical conductance (g(TE)) and ion transport (as indicated by short-circuit current) across Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell monolayers in a time- and concentration-dependent manner when apically exposed. g(TE) increases from less than 2 to greater than 40 mS/cm(2) over the low to middle micromolar range. Dextran polymer (9.5 but not 77 kDa) permeates the monolayer following apical NC-1059 exposure, suggesting that modulation of the paracellular pathway accounts for changes in g(TE). However, concomitant alterations in junctional protein localization (zonula occludens-1, occludin) and cellular morphology are not observed. Effects of NC-1059 on MDCK g(TE) occur in nominally Cl(-)- and Na(+)-free apical media, indicating that permeation by these ions is not required for effects on g(TE), although two-electrode voltage-clamp assays with Xenopus oocytes suggest that both Cl(-) and Na(+) permeate NC-1059 channels with a modest Cl(-) permselectivity (P(Cl):P(Na) = 1.3). MDCK monolayers can be exposed to multiple NC-1059 treatments over days to weeks without diminution of response, alteration in the time course, or loss of responsiveness to physiological and pharmacological secretagogues. Together, these results suggest that NC-1059 represents a valuable tool to investigate tight junction regulation and may be a lead compound for therapeutic interventions. | 15151917
 |