A functional yeast survival screen of tumor-derived cDNA libraries designed to identify anti-apoptotic mammalian oncogenes.
Eißmann, M; Schwamb, B; Melzer, IM; Moser, J; Siele, D; Köhl, U; Rieker, RJ; Wachter, DL; Agaimy, A; Herpel, E; Baumgarten, P; Mittelbronn, M; Rakel, S; Kögel, D; Böhm, S; Gutschner, T; Diederichs, S; Zörnig, M
PloS one
8
e64873
2013
Show Abstract
Yeast cells can be killed upon expression of pro-apoptotic mammalian proteins. We have established a functional yeast survival screen that was used to isolate novel human anti-apoptotic genes overexpressed in treatment-resistant tumors. The screening of three different cDNA libraries prepared from metastatic melanoma, glioblastomas and leukemic blasts allowed for the identification of many yeast cell death-repressing cDNAs, including 28% of genes that are already known to inhibit apoptosis, 35% of genes upregulated in at least one tumor entity and 16% of genes described as both anti-apoptotic in function and upregulated in tumors. These results confirm the great potential of this screening tool to identify novel anti-apoptotic and tumor-relevant molecules. Three of the isolated candidate genes were further analyzed regarding their anti-apoptotic function in cell culture and their potential as a therapeutic target for molecular therapy. PAICS, an enzyme required for de novo purine biosynthesis, the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 and the MAST2 kinase are overexpressed in certain tumor entities and capable of suppressing apoptosis in human cells. Using a subcutaneous xenograft mouse model, we also demonstrated that glioblastoma tumor growth requires MAST2 expression. An additional advantage of the yeast survival screen is its universal applicability. By using various inducible pro-apoptotic killer proteins and screening the appropriate cDNA library prepared from normal or pathologic tissue of interest, the survival screen can be used to identify apoptosis inhibitors in many different systems. | | 23717670
 |
Disease-specific molecular events in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions.
Fischer, MT; Wimmer, I; Höftberger, R; Gerlach, S; Haider, L; Zrzavy, T; Hametner, S; Mahad, D; Binder, CJ; Krumbholz, M; Bauer, J; Bradl, M; Lassmann, H
Brain : a journal of neurology
136
1799-815
2013
Show Abstract
Cortical lesions constitute an important part of multiple sclerosis pathology. Although inflammation appears to play a role in their formation, the mechanisms leading to demyelination and neurodegeneration are poorly understood. We aimed to identify some of these mechanisms by combining gene expression studies with neuropathological analysis. In our study, we showed that the combination of inflammation, plaque-like primary demyelination and neurodegeneration in the cortex is specific for multiple sclerosis and is not seen in other chronic inflammatory diseases mediated by CD8-positive T cells (Rasmussen's encephalitis), B cells (B cell lymphoma) or complex chronic inflammation (tuberculous meningitis, luetic meningitis or chronic purulent meningitis). In addition, we performed genome-wide microarray analysis comparing micro-dissected active cortical multiple sclerosis lesions with those of tuberculous meningitis (inflammatory control), Alzheimer's disease (neurodegenerative control) and with cortices of age-matched controls. More than 80% of the identified multiple sclerosis-specific genes were related to T cell-mediated inflammation, microglia activation, oxidative injury, DNA damage and repair, remyelination and regenerative processes. Finally, we confirmed by immunohistochemistry that oxidative damage in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions is associated with oligodendrocyte and neuronal injury, the latter also affecting axons and dendrites. Our study provides new insights into the complex mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in the cortex of patients with multiple sclerosis. | | 23687122
 |
P2X7 receptor differentially modulates astroglial apoptosis and clasmatodendrosis in the rat brain following status epilepticus.
Ji-Eun Kim,Hea Jin Ryu,Seong-Il Yeo,Tae-Cheon Kang
Hippocampus
21
2011
Show Abstract
Recently, it has been reported that astroglial loss/dysfunction plays a role in epileptogenesis. In addition, astroglial loss is accompanied by up-regulation of P2X7 receptor expression in microglia. Therefore, we investigated whether P2X7 receptor is involved in astroglial damages induced by status epilepticus (SE). In the present study, astroglial loss showed the regional-specific manner and the differential responses to P2X7 receptor functions. Both OxATP and brilliant blue G (P2X7 receptor antagonists) infusion prevented apoptotic astroglial loss in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus and the frontoparietal cortex, while it promoted clasmatodendrosis in the CA1 region as compared to saline treatment. In contrast, BzATP (a P2X7 receptor agonist) treatment exacerbated apoptotic astroglial loss in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus and the frontoparietal cortex, but alleviated SE-induced astroglial swelling in the CA1 region. Astroglial loss in the piriform cortex was not affected by P2X7 receptor agonist- or antagonist-infusion. These findings suggest that P2X7 receptor function differently modulates SE-induced astroglial loss in distinct brain regions. | | 20848604
 |
Caspase-3 deficiency reveals a physiologic role for Smac/DIABLO in regulating programmed cell death.
Hui, KK; Kanungo, AK; Elia, AJ; Henderson, JT
Cell death and differentiation
18
1780-90
2011
Show Abstract
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)-binding proteins such as Grim, Reaper and HID have been shown to exert a critical role in regulating caspase activity in species such as D. Melanogaster. However, a comparable role for the mammalian homologue of second mitochondrial-derived activator of caspase/direct IAP-binding protein with low pI (Smac/DIABLO) has yet to be clearly established in vivo. Despite tremendous interest in recent years in the use of so-called Smac mimetics to enhance chemotherapeutic potency, our understanding of the true physiologic nature of Smac/DIABLO in regulating programmed cell death (PCD) remains elusive. In order to critically evaluate the role of Smac/DIABLO in regulating mammalian PCD, deficiency of caspase-3 was used as a sensitizing mutation in order to reduce aggregate levels of executioner caspase activity. We observe that combinatorial deletion of Diablo and Casp3, but neither alone, results in perinatal lethality in mice. Consistent with this, examination of both intrinsic and extrinsic forms of PCD in lines of murine embryonic fibroblasts demonstrate that loss of Smac/DIABLO alters both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent intrinsic PCD. Comparative small interfering RNA inhibition studies of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis (cIAP)-1, cIAP-2, caspase-6 and -7 in both wild-type and Casp3/Diablo DKO mouse embryonic fibroblast lineages, supports a model in which Smac/DIABLO acts to enhance the early phase executioner caspase activity through the modulation of inhibitory interactions between specific IAP family members and executioner caspases-3 and -7. | | 21597464
 |
Inhibition of apoptosome activation protects injured motor neurons from cell death.
Kanungo, AK; Hao, Z; Elia, AJ; Mak, TW; Henderson, JT
The Journal of biological chemistry
283
22105-12
2008
Show Abstract
Within the mammalian central nervous system many forms of neurodegenerative injury are regulated via programmed cell death, a highly conserved program of cellular suicide. Programmed cell death is regulated by multiple signaling pathways, which have been identified within mammalian cells, although several lines of evidence suggest that the intrinsic pathway predominantly regulates the death of motor neurons following acute injury in vivo. We have tested this hypothesis by performing facial axotomies on cytochrome c knock-in mice containing a point mutation in the genomic locus of cytochrome c resulting in a lysine to alanine conversion at position 72 of the protein. The introduced mutation inhibits the ability of cytochrome c to induce the formation of the apoptosome, a protein complex that is principally required for the activation of the intrinsic pathway, but does not alter its function in oxidative phosphorylation. Homozygous cytochrome c knock-in mutants displayed a significant enhancement in motor neuron survival following injury when compared with littermate controls, thus establishing the apoptosome as a viable target for protecting motor neurons from neural injury. However, protection of facial motor neurons differs from that previously reported in mice either overexpressing anti-apoptotic or lacking pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, which are thought to regulate several aspects of mitochondrial dysfunction including the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm. Therefore, these results directly demonstrate for the first time the influence of the apoptosome on injury-induced neuronal programmed cell death in vivo isolated from upstream Bcl-2 family-mediated effects. | Immunohistochemistry | 18550520
 |
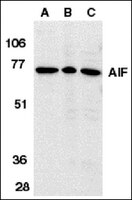
4-hydroperoxy-cyclophosphamide mediates caspase-independent T-cell apoptosis involving oxidative stress-induced nuclear relocation of mitochondrial apoptogenic factors AIF and EndoG.
Strauss, G; Westhoff, MA; Fischer-Posovszky, P; Fulda, S; Schanbacher, M; Eckhoff, SM; Stahnke, K; Vahsen, N; Kroemer, G; Debatin, KM
Cell death and differentiation
15
332-43
2008
Show Abstract
Apoptosis is a major mechanism of treatment-induced T-cell depletion in leukemia and autoimmune diseases. While 'classical' apoptosis is considered to depend on caspase activation, caspase-independent death is increasingly recognized as an alternative pathway. Although the DNA-damaging drug cyclophosphamide (CY) is widely used for therapy of hematological malignancies and autoimmune disorders, the molecular mechanism of apoptosis induction remains largely unknown. Here, we report that treatment of Jurkat, cytotoxic, and primary leukemic T cells with an activated analog of CY, 4-hydroperoxy-cyclophosphamide (4-OOH-CY), induces caspase activation and typical features of apoptosis, although cell death was not prevented by caspase inhibition. Also depletion of murine thymocytes and splenocytes after CY treatment in vivo was not inhibited by Z-Val-Ala-DL-Asp-fluoromethylketone (Z-VAD.fmk). Caspase-8 and receptor-induced protein (RIP) were dispensable for 4-OOH-CY-mediated apoptosis, while overexpression of Bcl-2 was partially protective. 4-OOH-CY treatment induced reactive oxygen species production, upregulation of Bax, and nuclear relocation of the mitochondrial factors apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and endonuclease G (EndoG). The antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine substantially inhibited conformational changes of Bax, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, nuclear relocation of mitochondrial factors, and apoptosis induction in 4-OOH-CY-treated T cells. These results strongly indicate that oxidative damage-induced nuclear translocation of AIF and EndoG in 4-OOH-CY-treated T cells might represent an alternative death pathway in the absence of caspase activity. | | 18034189
 |
Griffonia simplicifolia isolectin B4 identifies a specific subpopulation of angiogenic blood vessels following contusive spinal cord injury in the adult mouse.
Benton, RL; Maddie, MA; Minnillo, DR; Hagg, T; Whittemore, SR
The Journal of comparative neurology
507
1031-52
2008
Show Abstract
After traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI), disruption and plasticity of the microvasculature within injured spinal tissue contribute to the pathological cascades associated with the evolution of both primary and secondary injury. Conversely, preserved vascular function most likely results in tissue sparing and subsequent functional recovery. It has been difficult to identify subclasses of damaged or regenerating blood vessels at the cellular level. Here, adult mice received a single intravenous injection of the Griffonia simplicifolia isolectin B4 (IB4) at 1-28 days following a moderate thoracic (T9) contusion. Vascular binding of IB4 was maximally observed 7 days following injury, a time associated with multiple pathologic aspects of the intrinsic adaptive angiogenesis, with numbers of IB4 vascular profiles decreasing by 21 days postinjury. Quantitative assessment of IB4 binding shows that it occurs within the evolving lesion epicenter, with affected vessels expressing a temporally specific dysfunctional tight junctional phenotype as assessed by occludin, claudin-5, and ZO-1 immunoreactivities. Taken together, these results demonstrate that intravascular lectin delivery following SCI is a useful approach not only for observing the functional status of neovascular formation but also for definitively identifying specific subpopulations of reactive spinal microvascular elements. | | 18092342
 |
Mitochondrial control of cell death induced by hyperosmotic stress.
Criollo, A; Galluzzi, L; Maiuri, MC; Tasdemir, E; Lavandero, S; Kroemer, G
Apoptosis : an international journal on programmed cell death
12
3-18
2007
Show Abstract
HeLa and HCT116 cells respond differentially to sorbitol, an osmolyte able to induce hypertonic stress. In these models, sorbitol promoted the phenotypic manifestations of early apoptosis followed by complete loss of viability in a time-, dose-, and cell type-specific fashion, by eliciting distinct yet partially overlapping molecular pathways. In HCT116 but not in HeLa cells, sorbitol caused the mitochondrial release of the caspase-independent death effector AIF, whereas in both cell lines cytochrome c was retained in mitochondria. Despite cytochrome c retention, HeLa cells exhibited the progressive activation of caspase-3, presumably due to the prior activation of caspase-8. Accordingly, caspase inhibition prevented sorbitol-induced killing in HeLa, but only partially in HCT116 cells. Both the knock-out of Bax in HCT116 cells and the knock-down of Bax in A549 cells by RNA interference reduced the AIF release and/or the mitochondrial alterations. While the knock-down of Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) sensitized to sorbitol-induced killing, overexpression of a Bcl-2 variant that specifically localizes to mitochondria (but not of the wild-type nor of a endoplasmic reticulum-targeted form) strongly inhibited sorbitol effects. Thus, hyperosmotic stress kills cells by triggering different molecular pathways, which converge at mitochondria where pro- and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family exert their control. | | 17080328
 |
Physical interaction of apoptosis-inducing factor with DNA and RNA.
Vahsen, N; Candé, C; Dupaigne, P; Giordanetto, F; Kroemer, RT; Herker, E; Scholz, S; Modjtahedi, N; Madeo, F; Le Cam, E; Kroemer, G
Oncogene
25
1763-74
2006
Show Abstract
Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is a mitochondrial flavoprotein, which upon apoptosis induction translocates to the nucleus where it interacts with DNA by virtue of positive charges clustered on the AIF surface. Here we show that the AIF interactome, as determined by mass spectroscopy, contains a large panel of ribonucleoproteins, which apparently bind to AIF through the RNA moiety. However, AIF is devoid of any detectable RNAse activity both in vitro and in vivo. Recombinant AIF can directly bind to DNA as well as to RNA. This binding can be visualized by electron microscopy, revealing that AIF can condense DNA, showing a preferential binding to single-stranded over double-stranded DNA. AIF also binds and aggregates single-stranded and structured RNA in vitro. Single-stranded poly A, poly G and poly C, as well double-stranded A/T and G/C RNA competed with DNA for AIF binding with a similar efficiency, thus corroborating a computer-calculated molecular model in which the binding site within AIF is the same for distinct nucleic acid species, without a clear sequence specificity. Among the preferred electron donors and acceptors of AIF, nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) was particularly efficient in enhancing the generation of higher-order AIF/DNA and AIF/RNA complexes. Altogether, these data support a model in which a direct interaction of AIF contributes to the compaction of nucleic acids within apoptotic cells. | | 16278674
 |
Loss of Aif function causes cell death in the mouse embryo, but the temporal progression of patterning is normal.
Brown, D; Yu, BD; Joza, N; Bénit, P; Meneses, J; Firpo, M; Rustin, P; Penninger, JM; Martin, GR
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
103
9918-23
2006
Show Abstract
Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is an evolutionarily conserved, ubiquitously expressed flavoprotein with NADH oxidase activity that is normally confined to mitochondria. In mammalian cells, AIF is released from mitochondria in response to apoptotic stimuli and translocates to the nucleus where it is thought to bind DNA and contribute to chromatinolysis and cell death in a caspase-independent manner. Here we describe the consequences of inactivating Aif in the early mouse embryo. Unexpectedly, we found that both the apoptosis-dependent process of cavitation in embryoid bodies and apoptosis associated with embryonic neural tube closure occur in the absence of AIF, indicating that Aif function is not required for apoptotic cell death in early mouse embryos. By embryonic day 9 (E9), loss of Aif function causes abnormal cell death, presumably because of reduced mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I activity. Because of this cell death, Aif null embryos fail to increase significantly in size after E9. Remarkably, patterning processes continue on an essentially normal schedule, such that E10 Aif null embryos with only approximately 1/10 the normal number of cells have the same somite number as their wild-type littermates. These observations show that pattern formation in the mouse can occur independent of embryo size and cell number. Full Text Article | | 16788063
 |