Protective effects of lipocalin-2 (LCN2) in acute liver injury suggest a novel function in liver homeostasis.
Borkham-Kamphorst, E; van de Leur, E; Zimmermann, HW; Karlmark, KR; Tihaa, L; Haas, U; Tacke, F; Berger, T; Mak, TW; Weiskirchen, R
Biochimica et biophysica acta
1832
660-73
2013
Show Abstract
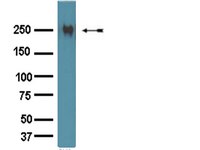
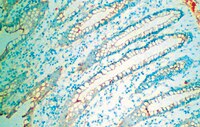
Lipocalin-2 is expressed under pernicious conditions such as intoxication, infection, inflammation and other forms of cellular stress. Experimental liver injury induces rapid and sustained LCN2 production by injured hepatocytes. However, the precise biological function of LCN2 in liver is still unknown. In this study, LCN2(-/-) mice were exposed to short term application of CCl4, lipopolysaccharide and Concanavalin A, or subjected to bile duct ligation. Subsequent injuries were assessed by liver function analysis, qRT-PCR for chemokine and cytokine expression, liver tissue Western blot, histology and TUNEL assay. Serum LCN2 levels from patients suffering from liver disease were assessed and evaluated. Acute CCl4 intoxication showed increased liver damage in LCN2(-/-) mice indicated by higher levels of aminotransferases, and increased expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and MCP-1/CCL2, resulting in sustained activation of STAT1, STAT3 and JNK pathways. Hepatocytes of LCN2(-/-) mice showed lipid droplet accumulation and increased apoptosis. Hepatocyte apoptosis was confirmed in the Concanavalin A and lipopolysaccharide models. In chronic models (4weeks bile duct ligation or 8weeks CCl4 application), LCN2(-/-) mice showed slightly increased fibrosis compared to controls. Interestingly, serum LCN2 levels in diseased human livers were significantly higher compared to controls, but no differences were observed between cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients. Upregulation of LCN2 is a reliable indicator of liver damage and has significant hepato-protective effect in acute liver injury. LCN2 levels provide no correlation to the degree of liver fibrosis but show significant positive correlation to inflammation instead. | Immunohistochemistry | | 23376114
 |
Chronic and intermittent hypoxia differentially regulate left ventricular inflammatory and extracellular matrix responses.
Ramirez, TA; Jourdan-Le Saux, C; Joy, A; Zhang, J; Dai, Q; Mifflin, S; Lindsey, ML
Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension
35
811-8
2012
Show Abstract
We evaluated the left ventricle (LV) response to hypoxia by comparing male Sprague Dawley rats exposed for 7 days to normoxia (control; n=18), chronic sustained hypoxia (CSH; n=12) and chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH; n=12). Out of the 168 inflammatory, extracellular matrix and adhesion molecule genes evaluated, Ltb, Cdh4, Col5a1, Ecm1, MMP-11 and TIMP-2 increased in the LV (range: 87-138%), whereas Tnfrsf1a decreased 27%, indicating an increase in inflammatory status with CSH (all Pless than 0.05). CIH decreased Ltb, Spp1 and Ccl5 levels, indicating reduced inflammatory status. While Laminin β2 gene levels increased 123%, MMP-9 and fibronectin gene levels both decreased 74% in CIH (all Pless than 0.05). Right ventricle/body weight ratios increased in CSH (1.1±0.1 g g(-1)) compared with control (0.7±0.1 g g(-1)) and CIH (0.8±0.1 g g(-1); both Pless than 0.05). Lung to body weight increased in CSH, while LV/body weight ratios were similar among all three groups. With CIH, myocyte cross sectional areas increased 25% and perivascular fibrosis increased 100% (both Pless than 0.05). Gene changes were independent of global changes and were validated by protein levels. MMP-9 protein levels decreased 94% and fibronectin protein levels decreased 42% in CIH (both Pless than 0.05). Consistent with a decreased inflammatory status, HIF-2α and eNOS protein levels were 36% and 44% decreased, respectively, in CIH (both Pless than 0.05). In conclusion, our results indicate that following 7 days of hypoxia, inflammation increases in response to CSH and decreases in response to CIH. This report is the first to demonstrate specific and differential changes seen in the LV during chronic sustained and CIH. | Western Blotting | Rat | 22495609
 |
CCN3/NOV small interfering RNA enhances fibrogenic gene expression in primary hepatic stellate cells and cirrhotic fat storing cell line CFSC.
Borkham-Kamphorst, E; van Roeyen, CR; Van de Leur, E; Floege, J; Weiskirchen, R
Journal of cell communication and signaling
6
11-25
2012
Show Abstract
Nephroblastoma overexpressed gene encodes a matricellular protein (CCN3/NOV) of the CCN family, comprising CCN1 (CYR61), CCN2 (CTGF), CCN4 (WISP-1), CCN5 (WISP-2), and CCN6 (WISP-3). CCN proteins are involved in the regulation of mitosis, adhesion, apoptosis, extracellular matrix production, growth arrest and migration in multiple cell types. Compared to CCN2/CTGF, known as a profibrotic protein, the biological role of CCN3/NOV in liver fibrosis remains obscure. In this study we showed ccn3/nov mRNA to increase dramatically following hepatic stellate cell activation, reaching peak levels in fully transdifferentiated myofibroblasts. In models of experimental hepatic fibrosis, CCN3/NOV increased significantly at the mRNA and protein levels. CCN3/NOV was found mainly in non-parenchymal cells along the areas of tissue damage and repair. In the bile-duct ligation model, CCN3/NOV was localized mainly along portal tracts, while the repeated application of carbon tetrachloride resulted in CCN3/NOV expression mainly in the centrilobular areas. In contrast to CCN2/CTGF, the profibrotic cytokines platelet-derived growth factor-B and -D as well as transforming growth factor-β suppressed CCN3/NOV expression. In vitro, CCN3/NOV siRNA attenuated migration in the cirrhotic fat storing cell line CFSC well in line with in vivo findings that various types of cells expressing CCN3/NOV migrate into the area of tissue damage and regeneration. The suppression of CCN3/NOV enhanced expression of profibrotic marker proteins, such as α-smooth muscle actin, collagen type I, fibronectin, CCN2/CTGF and TIMP-1 in primary rat hepatic stellate cells and in CFSC. We further found that adenoviral overexpression of CCN2/CTGF suppressed CCN3/NOV expression, while the overexpression of CCN3/NOV as well as the suppression of CCN3/NOV by targeting siRNAs both resulted in enhanced CCN2/CTGF expression. These results indicate the complexity of CCN actions that are far beyond the classic Yin/Yang interplay. | | | 21748432
 |
SPARC mediates early extracellular matrix remodeling following myocardial infarction.
McCurdy, SM; Dai, Q; Zhang, J; Zamilpa, R; Ramirez, TA; Dayah, T; Nguyen, N; Jin, YF; Bradshaw, AD; Lindsey, ML
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology
301
H497-505
2011
Show Abstract
Secreted protein, acidic, and rich in cysteine (SPARC) is a matricellular protein that functions in the extracellular processing of newly synthesized collagen. Collagen deposition to form a scar is a key event following a myocardial infarction (MI). Because the roles of SPARC in the early post-MI setting have not been defined, we examined age-matched wild-type (WT; n=22) and SPARC-deficient (null; n=25) mice at day 3 post-MI. Day 0 WT (n=28) and null (n=20) mice served as controls. Infarct size was 52 ± 2% for WT and 47 ± 2% for SPARC null (P=NS), indicating that the MI injury was comparable in the two groups. By echocardiography, WT mice increased end-diastolic volumes from 45 ± 2 to 83 ± 5 μl (P less than 0.05). SPARC null mice also increased end-diastolic volumes but to a lesser extent than WT (39 ± 3 to 63 ± 5 μl; P less than 0.05 vs. day 0 controls and vs. WT day 3 MI). Ejection fraction fell post-MI in WT mice from 57 ± 2 to 19 ± 1%. The decrease in ejection fraction was attenuated in the absence of SPARC (65 ± 2 to 28 ± 2%). Fibroblasts isolated from SPARC null left ventricle (LV) showed differences in the expression of 22 genes encoding extracellular matrix and adhesion molecule genes, including fibronectin, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF; CCN2), matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2). The change in fibroblast gene expression levels was mirrored in tissue protein extracts for fibronectin, CTGF, and MMP-3 but not TIMP-2. Combined, the results of this study indicate that SPARC deletion preserves LV function at day 3 post-MI but may be detrimental for the long-term response due to impaired fibroblast activation. | | | 21602472
 |
Correction: cross-sample validation provides enhanced proteome coverage in rat vocal fold mucosa.
Welham NV, Yamashita M, Choi SH, Ling C
PLoS One
6
2011
Show Abstract
[This corrects the article on p. e17754 in vol. 6.]. | | | 21479201
 |
Cross-sample validation provides enhanced proteome coverage in rat vocal fold mucosa.
Welham, NV; Yamashita, M; Choi, SH; Ling, C
PloS one
6
e17754
2011
Show Abstract
The vocal fold mucosa is a biomechanically unique tissue comprised of a densely cellular epithelium, superficial to an extracellular matrix (ECM)-rich lamina propria. Such ECM-rich tissues are challenging to analyze using proteomic assays, primarily due to extensive crosslinking and glycosylation of the majority of high M(r) ECM proteins. In this study, we implemented an LC-MS/MS-based strategy to characterize the rat vocal fold mucosa proteome. Our sample preparation protocol successfully solubilized both proteins and certain high M(r) glycoconjugates and resulted in the identification of hundreds of mucosal proteins. A straightforward approach to the treatment of protein identifications attributed to single peptide hits allowed the retention of potentially important low abundance identifications (validated by a cross-sample match and de novo interpretation of relevant spectra) while still eliminating potentially spurious identifications (global single peptide hits with no cross-sample match). The resulting vocal fold mucosa proteome was characterized by a wide range of cellular and extracellular proteins spanning 12 functional categories. Full Text Article | | | 21423617
 |
Induction of lipocalin-2 expression in acute and chronic experimental liver injury moderated by pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β through nuclear factor-κB activation.
Borkham-Kamphorst E, Drews F, Weiskirchen R
Liver Int
31
656-65. doi
2011
Show Abstract
Background: Lipocalin-2 (LCN2) belongs to the lipocalin superfamily, sharing a barrel-shaped tertiary structure with a hydrophobic pocket and an ability to bind lipophilic molecules. LCN2 has recently emerged as an important modulator of cellular homeostasis in several organs, i.e. heart, lung and kidney, but little is known about the expression of LCN2 in acute and chronic liver injury. Aims: In this study, we wanted to analyse the expression and regulation of LCN2 in models of acute and chronic experimental liver injury. Materials and methods: We analysed LCN2 expression in livers of rats subjected to bile duct ligation or repeated doses of carbon tetrachloride and tested the impact of various pro-inflammatory cytokines in cultured primary liver cells. Results: By using primary cultures of hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes isolated from normal and injured rat livers, we found a significant LCN2 expression in early hepatic stellate cell cultures, a lower expression in fully transdifferentiated myofibroblasts and no expression in freshly isolated hepatocytes. However, LCN2 expression and secretion in hepatocytes increased dramatically during culturing. In addition, chronic in vivo liver injury resulting from both bile duct ligation and repeated application of carbon tetrachloride resulted in rapid and well-sustained induction of LCN2 expression. Immunohistochemistry and primary liver cell isolation identified injured hepatocytes as the main source of LCN2 production. LCN2 is strongly induced in both primary hepatocytes and immortalized hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 by the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β via nuclear factor-κB activation, but not by the profibrotic cytokines platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-β. Conclusion: LCN2 expression shows clear correlation to liver damage and resulting inflammatory responses, rather than to the degree of liver fibrosis, which in fact may imply a distinct diagnostic value as an early biomarker of liver inflammation.© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S. | | | 21457438
 |
Mesenchymal stem cell responses to bone-mimetic electrospun matrices composed of polycaprolactone, collagen I and nanoparticulate hydroxyapatite.
Phipps, MC; Clem, WC; Catledge, SA; Xu, Y; Hennessy, KM; Thomas, V; Jablonsky, MJ; Chowdhury, S; Stanishevsky, AV; Vohra, YK; Bellis, SL
PloS one
6
e16813
2011
Show Abstract
The performance of biomaterials designed for bone repair depends, in part, on the ability of the material to support the adhesion and survival of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In this study, a nanofibrous bone-mimicking scaffold was electrospun from a mixture of polycaprolactone (PCL), collagen I, and hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles with a dry weight ratio of 50/30/20 respectively (PCL/col/HA). The cytocompatibility of this tri-component scaffold was compared with three other scaffold formulations: 100% PCL (PCL), 100% collagen I (col), and a bi-component scaffold containing 80% PCL/20% HA (PCL/HA). Scanning electron microscopy, fluorescent live cell imaging, and MTS assays showed that MSCs adhered to the PCL, PCL/HA and PCL/col/HA scaffolds, however more rapid cell spreading and significantly greater cell proliferation was observed for MSCs on the tri-component bone-mimetic scaffolds. In contrast, the col scaffolds did not support cell spreading or survival, possibly due to the low tensile modulus of this material. PCL/col/HA scaffolds adsorbed a substantially greater quantity of the adhesive proteins, fibronectin and vitronectin, than PCL or PCL/HA following in vitro exposure to serum, or placement into rat tibiae, which may have contributed to the favorable cell responses to the tri-component substrates. In addition, cells seeded onto PCL/col/HA scaffolds showed markedly increased levels of phosphorylated FAK, a marker of integrin activation and a signaling molecule known to be important for directing cell survival and osteoblastic differentiation. Collectively these results suggest that electrospun bone-mimetic matrices serve as promising degradable substrates for bone regenerative applications. Full Text Article | | | 21346817
 |
Proteomic analysis identifies in vivo candidate matrix metalloproteinase-9 substrates in the left ventricle post-myocardial infarction.
Rogelio Zamilpa,Elizabeth F Lopez,Ying Ann Chiao,Qiuxia Dai,Gladys P Escobar,Kevin Hakala,Susan T Weintraub,Merry L Lindsey
Proteomics
10
2010
Show Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) deletion has been shown to improve remodeling of the left ventricle post-myocardial infarction (MI), but the mechanisms to explain this improvement have not been fully elucidated. MMP-9 has a broad range of in vitro substrates, but relevant in vivo substrates are incompletely defined. Accordingly, we evaluated the infarct regions of wild-type (wt) and MMP-9 null (null) mice using a proteomic strategy. Wt and null groups showed similar infarct sizes (48+/-3 in wt and 45+/-3% in null), indicating that both groups received an equal injury stimulus. Left ventricle infarct tissue was homogenized and analyzed by 2-DE and MS. Of 31 spot intensity differences, the intensities of 9 spots were higher and 22 spots were lower in null mice compared to wt (all p<0.05). Several extracellular matrix proteins were identified in these spots by MS, including fibronectin, tenascin-C, thrombospondin-1, and laminin. Fibronectin was observed on the gels at a lower than expected molecular weight in the wt group, which suggested substrate cleavage, and the lower molecular weight spot was observed at lower intensity in the MMP-9 null group, which suggested cleavage by MMP-9. Immunoblotting confirmed the presence of fibronectin cleavage products in the wt samples and lower levels in the absence of MMP-9. In conclusion, examining infarct tissue from wt and MMP-9 null mice by proteomic analysis provides a powerful and unique method to identify in vivo candidate MMP substrates. Full Text Article | | | 20354994
 |
Vascular effects of cardiotrophin-1: a role in hypertension?
Lopez-Andres, Natalia, et al.
J. Hypertens., 28: 1261-72 (2010)
2010
Show Abstract
AIMS: To investigate cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) effects and regulation in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) in vitro and in aortic tunica media ex vivo in normotensive Wistar rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). METHODS AND RESULTS: CT-1 expression was quantified by real-time reverse-transcription PCR and western blotting. CT-1-activated intracellular pathways were assessed by western bloting analysis. Proliferation was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay and ki67 immunodetection, and cell hypertrophy by planimetry. Extracellular matrix components were quantified by real-time reverse-transcription PCR and western blot, and metalloproteinases activities by zymography. VSMCs from Wistar rats and SHRs expressed spontaneously CT-1 at the mRNA and the protein level, with a two-fold more increase in SHRs. CT-1 phosphorylated p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, Akt and Stat-3 in both strains. CT-1 stimulated VSMCs proliferation and hypertrophy in both strains, with an enhanced stimulation in SHRs. CT-1 increased the secretion of collagen type I and fibronectin in VSMCs and aortic tunica media of Wistar rats and SHRs, with greater magnitude in SHRs. In SHRs VSMCs in vitro and ex vivo, CT-1 increased the secretion of collagen type III and elastin and the expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, without altering metalloproteinase activity. These effects were blocked by CT-1 receptor antibodies. Aldosterone treatment increased CT-1 expression in VSMCs and aortic tunica media from both strains, with a greater magnitude in SHRs. CONCLUSION: CT-1 induces VSMCs proliferation, hypertrophy and extracellular matrix production, and is upregulated in hypertension and by aldosterone. CT-1 may represent a new target of vascular wall remodeling in hypertension. | | | 20216087
 |