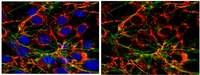
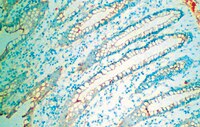
L-Endoglin overexpression increases renal fibrosis after unilateral ureteral obstruction.
Oujo, B; Muñoz-Félix, JM; Arévalo, M; Núñez-Gómez, E; Pérez-Roque, L; Pericacho, M; González-Núñez, M; Langa, C; Martínez-Salgado, C; Perez-Barriocanal, F; Bernabeu, C; Lopez-Novoa, JM
PloS one
9
e110365
2014
Show Abstract
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) plays a pivotal role in renal fibrosis. Endoglin, a 180 KDa membrane glycoprotein, is a TGF-β co-receptor overexpressed in several models of chronic kidney disease, but its function in renal fibrosis remains uncertain. Two membrane isoforms generated by alternative splicing have been described, L-Endoglin (long) and S-Endoglin (short) that differ from each other in their cytoplasmic tails, being L-Endoglin the most abundant isoform. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of L-Endoglin overexpression in renal tubulo-interstitial fibrosis. For this purpose, a transgenic mouse which ubiquitously overexpresses human L-Endoglin (L-ENG+) was generated and unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) was performed in L-ENG+ mice and their wild type (WT) littermates. Obstructed kidneys from L-ENG+ mice showed higher amounts of type I collagen and fibronectin but similar levels of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) than obstructed kidneys from WT mice. Smad1 and Smad3 phosphorylation were significantly higher in obstructed kidneys from L-ENG+ than in WT mice. Our results suggest that the higher increase of renal fibrosis observed in L-ENG+ mice is not due to a major abundance of myofibroblasts, as similar levels of α-SMA were observed in both L-ENG+ and WT mice, but to the higher collagen and fibronectin synthesis by these fibroblasts. Furthermore, in vivo L-Endoglin overexpression potentiates Smad1 and Smad3 pathways and this effect is associated with higher renal fibrosis development. | Western Blotting | 25313562
 |
Complex contributions of fibronectin to initiation and maturation of microfibrils.
Sabatier, L; Djokic, J; Fagotto-Kaufmann, C; Chen, M; Annis, DS; Mosher, DF; Reinhardt, DP
The Biochemical journal
456
283-95
2013
Show Abstract
Fibrillins constitute the backbone of extracellular multifunctional assemblies present in elastic and non-elastic matrices, termed microfibrils. Assembly of fibrillins into microfibrils and their homoeostasis is poorly understood and is often compromised in connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome and other fibrillinopathies. Using interaction mapping studies, we demonstrate that fibrillins require the complete gelatin-binding region of fibronectin for interaction, which comprises domains FNI6-FNI9. However, the interaction of fibrillin-1 with the gelatin-binding domain of fibronectin is not involved in fibrillin-1 network assembly mediated by human skin fibroblasts. We show further that the fibronectin network is essential for microfibril homoeostasis in early stages. Fibronectin is present in extracted mature microfibrils from tissue and cells as well as in some in situ microfibrils observed at the ultrastructural level, indicating an extended mechanism for the involvement of fibronectin in microfibril assembly and maturation. | | 24070235
 |
Spatial and temporal analysis of extracellular matrix proteins in the developing murine heart: a blueprint for regeneration.
Hanson, KP; Jung, JP; Tran, QA; Hsu, SP; Iida, R; Ajeti, V; Campagnola, PJ; Eliceiri, KW; Squirrell, JM; Lyons, GE; Ogle, BM
Tissue engineering. Part A
19
1132-43
2013
Show Abstract
The extracellular matrix (ECM) of the embryonic heart guides assembly and maturation of cardiac cell types and, thus, may serve as a useful template, or blueprint, for fabrication of scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Surprisingly, characterization of the ECM with cardiac development is scattered and fails to comprehensively reflect the spatiotemporal dynamics making it difficult to apply to tissue engineering efforts. The objective of this work was to define a blueprint of the spatiotemporal organization, localization, and relative amount of the four essential ECM proteins, collagen types I and IV (COLI, COLIV), elastin (ELN), and fibronectin (FN) in the left ventricle of the murine heart at embryonic stages E12.5, E14.5, and E16.5 and 2 days postnatal (P2). Second harmonic generation (SHG) imaging identified fibrillar collagens at E14.5, with an increasing density over time. Subsequently, immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to compare the spatial distribution, organization, and relative amounts of each ECM protein. COLIV was found throughout the developing heart, progressing in amount and organization from E12.5 to P2. The amount of COLI was greatest at E12.5 particularly within the epicardium. For all stages, FN was present in the epicardium, with highest levels at E12.5 and present in the myocardium and the endocardium at relatively constant levels at all time points. ELN remained relatively constant in appearance and amount throughout the developmental stages except for a transient increase at E16.5. Expression of ECM mRNA was determined using quantitative polymerase chain reaction and allowed for comparison of amounts of ECM molecules at each time point. Generally, COLI and COLIII mRNA expression levels were comparatively high, while COLIV, laminin, and FN were expressed at intermediate levels throughout the time period studied. Interestingly, levels of ELN mRNA were relatively low at early time points (E12.5), but increased significantly by P2. Thus, we identified changes in the spatial and temporal localization of the primary ECM of the developing ventricle. This characterization can serve as a blueprint for fabrication techniques, which we illustrate by using multiphoton excitation photochemistry to create a synthetic scaffold based on COLIV organization at P2. Similarly, fabricated scaffolds generated using ECM components, could be utilized for ventricular repair. | Immunohistochemistry | 23273220
 |
Reelin controls neuronal positioning by promoting cell-matrix adhesion via inside-out activation of integrin α5β1.
Sekine, K; Kawauchi, T; Kubo, K; Honda, T; Herz, J; Hattori, M; Kinashi, T; Nakajima, K
Neuron
76
353-69
2012
Show Abstract
Birthdate-dependent neuronal layering is fundamental to neocortical functions. The extracellular protein Reelin is essential for the establishment of the eventual neuronal alignments. Although this Reelin-dependent neuronal layering is mainly established by the final neuronal migration step called "terminal translocation" beneath the marginal zone (MZ), the molecular mechanism underlying the control by Reelin of terminal translocation and layer formation is largely unknown. Here, we show that after Reelin binds to its receptors, it activates integrin α5β1 through the intracellular Dab1-Crk/CrkL-C3G-Rap1 pathway. This intracellular pathway is required for terminal translocation and the activation of Reelin signaling promotes neuronal adhesion to fibronectin through integrin α5β1. Since fibronectin is localized in the MZ, the activated integrin α5β1 then controls terminal translocation, which mediates proper neuronal alignments in the mature cortex. These data indicate that Reelin-dependent activation of neuronal adhesion to the extracellular matrix is crucial for the eventual birth-date-dependent layering of the neocortex. | | 23083738
 |
Combination therapy with an angiotensin II receptor blocker and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor in experimental subtotal nephrectomy.
Álvarez-Prats, A; Hernández-Perera, O; Díaz-Herrera, P; Ucero, ÁC; Anabitarte-Prieto, A; Losada-Cabrera, A; Ortiz, A; Rodríguez-Pérez, JC
Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association
27
2720-33
2012
Show Abstract
Angiotensin receptor 1 blockers (ARB) are standard nephroprotective drugs in chronic kidney disease. There is less evidence for a nephroprotective effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) and much less is known about potential benefits of combination therapy. We evaluated the therapeutic potential of a statin alone or in combination with an ARB in experimental chronic kidney disease.Subtotally nephrectomized (5/6 Nx) rats were treated early with vehicle, losartan, cerivastatin or losartan/cerivastatin. Expression of messenger RNA (mRNA) was assessed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Tissue proteins were localized by immunohistochemistry. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation was measured in whole kidneys.In contrast to the sham group, at 6 weeks, vehicle-treated 5/6 Nx rats displayed renal lesions, albuminuria and increased blood pressure, serum creatinine and total kidney NF-κB p65 DNA-binding activity and preproendothelin-1, fibronectin and type I and III collagen mRNA. NF-κB activation correlated with albuminuria and histological renal injury. Losartan or combination therapy preserved renal function, abrogated albuminuria and improved glomerular and interstitial histology. Cerivastatin alone preserved renal function and improved interstitial injury but did not influence albuminuria, glomerular histology or NF-κB activation. Losartan/cerivastatin normalized kidney NF-κB activation and extracellular matrix mRNA expression pattern. The effect of losartan alone on these parameters was less intense. All treatments decreased preproendothelin-1 mRNA and preserved interstitial capillaries.In a chronic kidney disease model, early treatment with either an ARB or a statin preserved renal function although the mechanisms differed. Combination therapy with an ARB and a statin did not confer clear-cut advantages on biochemical and histological parameters over ARB alone, although it further improved the kidney NF-κB and gene expression profile. | | 22302208
 |
A combinatorial extracellular matrix platform identifies cell-extracellular matrix interactions that correlate with metastasis.
Reticker-Flynn, NE; Malta, DF; Winslow, MM; Lamar, JM; Xu, MJ; Underhill, GH; Hynes, RO; Jacks, TE; Bhatia, SN
Nature communications
3
1122
2012
Show Abstract
Extracellular matrix interactions have essential roles in normal physiology and many pathological processes. Although the importance of extracellular matrix interactions in metastasis is well documented, systematic approaches to identify their roles in distinct stages of tumorigenesis have not been described. Here we report a novel-screening platform capable of measuring phenotypic responses to combinations of extracellular matrix molecules. Using a genetic mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma, we measure the extracellular matrix-dependent adhesion of tumour-derived cells. Hierarchical clustering of the adhesion profiles differentiates metastatic cell lines from primary tumour lines. Furthermore, we uncovered that metastatic cells selectively associate with fibronectin when in combination with galectin-3, galectin-8 or laminin. We show that these molecules correlate with human disease and that their interactions are mediated in part by α3β1 integrin. Thus, our platform allowed us to interrogate interactions between metastatic cells and their microenvironments, and identified extracellular matrix and integrin interactions that could serve as therapeutic targets. | Immunohistochemistry | 23047680
 |
Serum response factor is required for cell contact maintenance but dispensable for proliferation in visceral yolk sac endothelium.
Holtz, ML; Misra, RP
BMC developmental biology
11
18
2011
Show Abstract
Endothelial-specific knockout of the transcription factor serum response factor (SRF) results in embryonic lethality by mid-gestation. The associated phenotype exhibits vascular failure in embryos as well as visceral yolk sac (VYS) tissues. Previous data suggest that this vascular failure is caused by alterations in cell-cell and cell-matrix contacts. In the current study, we sought to more carefully address the role of SRF in endothelial function and cell contact interactions in VYS tissues.Tie2-Cre recombinase-mediated knockout of SRF expression resulted in loss of detectable SRF from VYS mesoderm by E12.5. This loss was accompanied by decreased expression of smooth muscle alpha-actin as well as vascular endothelial cadherin and claudin 5, endothelial-specific components of adherens and tight junctions, respectively. Focal adhesion (FA) integrins alpha5 and beta1 were largely unchanged in contrast to loss of the FA-associated molecule vinculin. The integrin binding partner fibronectin-1 was also profoundly decreased in the extracellular matrix, indicating another aspect of impaired adhesive function and integrin signaling. Additionally, cells in SRF-null VYS mesoderm failed to reduce proliferation, suggesting not only that integrin-mediated contact inhibition is impaired but also that SRF protein is not required for proliferation in these cells.Our data support a model in which SRF is critical in maintaining functional cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion in endothelial cells. Furthermore, we provide evidence that supports a model in which loss of SRF protein results in a sustained proliferation defect due in part to failed integrin signaling. Full Text Article | | 21401944
 |
Cutting Edge: mechanical forces acting on T cells immobilized via the TCR complex can trigger TCR signaling.
Li YC, Chen BM, Wu PC, Cheng TL, Kao LS, Tao MH, Lieber A, Roffler SR
J Immunol
184
5959-63. Epub 2010 Apr 30.
2010
Show Abstract
Engagement of the TCR by antigenic peptides presented by the MHC activates specific T cells to control infections. Recent theoretical considerations have suggested that mechanical forces acting on the TCR may be important for receptor triggering. In this study, we directly tested the hypothesis that physical forces acting on the TCR can initiate signaling in T cells by micromanipulation of individual T cells bound to artificial APCs expressing engineered TCR ligands. We find that mechanical forces acting on T cells bound to APCs via the TCR complex but not other surface receptors can initiate signaling in T cells in an Src kinase-dependent fashion. Our data indicate that T cells are mechanically sensitive when coupled to APCs by the TCR and indicates that the TCR may act as a mechanosensor. Our data provide new insight into TCR function. | | 20435924
 |
Ligand-specific function of transforming growth factor beta in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in heart development.
Azhar, M; Runyan, RB; Gard, C; Sanford, LP; Miller, ML; Andringa, A; Pawlowski, S; Rajan, S; Doetschman, T
Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists
238
431-42
2009
Show Abstract
The ligand specificity of transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) in vivo in mouse cardiac cushion epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is poorly understood. To elucidate the function of TGFbeta in cushion EMT, we analyzed Tgfb1(-/-), Tgfb2(-/-), and Tgfb3(-/-) mice between embryonic day (E) 9.5 and E14.5 using both in vitro and in vivo approaches. Atrioventricular (AV) canal collagen gel assays at E9.5 indicated normal EMT in both Tgfb1(-/-) and Tgfb3(-/-) mice. However, analysis of Tgfb2(-/-) AV explants at E9.5 and E10.5 indicated that EMT, but not cushion cell proliferation, was initially delayed but later remained persistent. This was concordant with the observation that Tgfb2(-/-) embryos, and not Tgfb1(-/-) or Tgfb3(-/-) embryos, develop enlarged cushions at E14.5 with elevated levels of well-validated indicators of EMT. Collectively, these data indicate that TGFbeta2, and not TGFbeta1 or TGFbeta3, mediates cardiac cushion EMT by promoting both the initiation and cessation of EMT. Full Text Article | | 19161227
 |
Activation of Erk1/2 and Akt following unilateral ureteral obstruction.
Rodríguez-Peña, AB; Grande, MT; Eleno, N; Arévalo, M; Guerrero, C; Santos, E; López-Novoa, JM
Kidney international
74
196-209
2008
Show Abstract
Chronic unilateral ureteral obstruction is a well characterized model of renal injury leading to tubulointerstitial fibrosis and distinct patterns of cell proliferation and apoptosis in the obstructed kidney. In this study we assessed the contribution of the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)-ERK1/2 and the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathways to early renal changes following unilateral obstruction. Increased activation of small Ras GTPase and its downstream effectors ERK1/2 and Akt was detected in ligated kidneys. The use of specific pharmacological inhibitors to either ERK1/2 or Akt activation led to decreased levels of fibroblast-myofibroblast markers in the interstitium while inhibition of PI3K reduced the number of proliferating cells and the amount of interstitial extracellular matrix deposition. Treatment with an ERK1/2 inhibitor diminished the number of apoptotic tubule and interstitial cells. Our results suggest a role for the MAPK-ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt systems in early changes induced by ureteral obstruction and that inhibition of these signaling pathways may provide a novel approach to prevent progression of renal fibrosis. | Western Blotting | 18449171
 |