Behavioral stress induces regionally-distinct shifts of brain mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor levels.
Caudal, D; Jay, TM; Godsil, BP
Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience
8
19
2014
Show Abstract
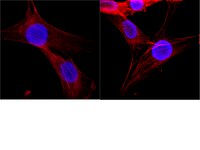
Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors (MRs and GRs) mediate the impact of stress on brain function primarily by affecting gene transcription in the cell nucleus. In vitro studies using hippocampal neurons indicate that MRs and GRs translocate to the nucleus after binding to the stress hormone corticosterone, yet the in vivo temporal dynamics of MR and GR levels in other limbic regions critical for the stress response, however, are largely unknown. Rats underwent an elevated platform (EP) stress procedure and brain tissue was sampled from the amygdala (AMY), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), dorsal hippocampus and ventral hippocampus. By measuring MR and GR levels in the nuclear fraction from the tissue sampled, we observed striking shifts in the protein levels that varied by receptor, brain region and by the time after EP stress. These findings indicate that the subcellular trafficking of corticosteroid receptors display distinct temporal dynamics in different limbic regions after behavioral stress. These heterogeneous effects could underlie contrasting regional responses to stress within the brain, and they highlight the importance for systems-level analysis of stress responsivity. | Western Blotting | 24523684
 |
Arabidopsis replacement histone variant H3.3 occupies promoters of regulated genes.
Shu, H; Nakamura, M; Siretskiy, A; Borghi, L; Moraes, I; Wildhaber, T; Gruissem, W; Hennig, L
Genome biology
15
R62
2014
Show Abstract
Histone variants establish structural and functional diversity of chromatin by affecting nucleosome stability and histone-protein interactions. H3.3 is an H3 histone variant that is incorporated into chromatin outside of S-phase in various eukaryotes. In animals, H3.3 is associated with active transcription and possibly maintenance of transcriptional memory. Plant H3 variants, which evolved independently of their animal counterparts, are much less well understood.We profile the H3.3 distribution in Arabidopsis at mono-nucleosomal resolution using native chromatin immunoprecipitation. This results in the precise mapping of H3.3-containing nucleosomes, which are not only enriched in gene bodies as previously reported, but also at a subset of promoter regions and downstream of the 3' ends of active genes. While H3.3 presence within transcribed regions is strongly associated with transcriptional activity, H3.3 at promoters is often independent of transcription. In particular, promoters with GA motifs carry H3.3 regardless of the gene expression levels. H3.3 on promoters of inactive genes is associated with H3K27me3 at gene bodies. In addition, H3.3-enriched plant promoters often contain RNA Pol II considerably upstream of the transcriptional start site. H3.3 and RNA Pol II are found on active as well as on inactive promoters and are enriched at strongly regulated genes.In animals and plants, H3.3 organizes chromatin in transcribed regions and in promoters. The results suggest a function of H3.3 in transcriptional regulation and support a model that a single ancestral H3 evolved into H3 variants with similar sub-functionalization patterns in plants and animals. | Immunoprecipitation | 24708891
 |
TNF stimulates nuclear export and secretion of IL-15 by acting on CRM1 and ARF6.
Ouyang, S; Hsuchou, H; Kastin, AJ; Pan, W
PloS one
8
e69356
2013
Show Abstract
Interleukin (IL)-15 is a ubiquitously expressed cytokine that in the basal state is mainly localized intracellularly, including the nucleus. Unexpectedly, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF) time-dependently induced nuclear export of IL-15Rα and IL15. This process was inhibited by leptomycine B (LMB), a specific inhibitor of nuclear export receptor chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1). In the presence of TNF, LMB co-treatment led to accumulation of both IL-15Rα and IL-15 in the nucleus of HeLa cells, suggesting that CRM1 facilitates nuclear export and that TNF enhances CRM1 activity. Once in the cytoplasm, IL-15 showed partial co-localization with late endosomes but very little with other organelles tested 4 h after TNF treatment. IL-15Rα showed co-localization with both early and late endosomes, and to a lesser extent with endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. This indicates different kinetics and possibly different trafficking routes of IL-15 from its specific receptor. The TNF-induced secretion of IL-15 was attenuated by pretreatment of cells by brefeldin A that inhibits ER-to-Golgi transport, or by use of domain negative ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) that interferes with exocytotic sorting. We conclude that TNF abolishes nuclear localization of IL-15 and IL-15Rα by acting on CRM1, and it facilitates exocytosis of IL-15 with the involvement of ARF6. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 23950892
 |
The responses of neural stem cells to the level of GSK-3 depend on the tissue of origin.
Holowacz, T; Alexson, TO; Coles, BL; Doble, BW; Kelly, KF; Woodgett, JR; Van Der Kooy, D
Biology open
2
812-21
2013
Show Abstract
Neural stem cells (NSCs) can be obtained from a variety of sources, but not all NSCs exhibit the same characteristics. We have examined how the level of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity regulates NSCs obtained from different sources: the mouse embryonic striatum, embryonic hippocampus, and mouse ES cells. Growth of striatal NSCs is enhanced by mild inhibition of GSK-3 but not by strong inhibition that is accompanied by Wnt/TCF transcriptional activation. In contrast, the growth of hippocampal NSCs is enhanced by both mild inhibition of GSK-3 as well as stronger inhibition. Active Wnt/TCF signaling, which occurs normally in the embryonic hippocampus, is required for growth of neural stem and progenitor cells. In the embryonic striatal germinal zone, however, TCF signaling is normally absent and its activation inhibits growth of NSCs from this region. Using a genetic model for progressive loss of GSK-3, we find that primitive ES cell-derived NSCs resemble striatal NSCs. That is, partial loss of GSK-3 alleles leads to an increase in NSCs while complete ablation of GSK-3, and activation of TCF-signaling, leads to their decline. Furthermore, expression of dominant negative TCF-4 in the GSK-3-null background was effective in blocking expression of Wnt-response genes and was also able to rescue neuronal gene expression. These results reveal that GSK-3 regulates NSCs by divergent pathways depending on the tissue of origin. The responses of these neural precursor cells may be contingent on baseline Wnt/TCF signaling occurring in a particular tissue. | | 23951407
 |
Global substrate profiling of proteases in human neutrophil extracellular traps reveals consensus motif predominantly contributed by elastase.
O'Donoghue, AJ; Jin, Y; Knudsen, GM; Perera, NC; Jenne, DE; Murphy, JE; Craik, CS; Hermiston, TW
PloS one
8
e75141
2013
Show Abstract
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) consist of antimicrobial molecules embedded in a web of extracellular DNA. Formation of NETs is considered to be a defense mechanism utilized by neutrophils to ensnare and kill invading pathogens, and has been recently termed NETosis. Neutrophils can be stimulated to undergo NETosis ex vivo, and are predicted to contain high levels of serine proteases, such as neutrophil elastase (NE), cathepsin G (CG) and proteinase 3 (PR3). Serine proteases are important effectors of neutrophil-mediated immunity, which function directly by degrading pathogenic virulent factors and indirectly via proteolytic activation or deactivation of cytokines, chemokines and receptors. In this study, we utilized a diverse and unbiased peptide library to detect and profile protease activity associated with NETs induced by phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA). We obtained a "proteolytic signature" from NETs derived from healthy donor neutrophils and used proteomics to assist in the identification of the source of this proteolytic activity. In addition, we profiled each neutrophil serine protease and included the newly identified enzyme, neutrophil serine protease 4 (NSP4). Each enzyme had overlapping yet distinct endopeptidase activities and often cleaved at unique sites within the same peptide substrate. The dominant proteolytic activity in NETs was attributed to NE; however, cleavage sites corresponding to CG and PR3 activity were evident. When NE was immunodepleted, the remaining activity was attributed to CG and to a lesser extent PR3 and NSP4. Our results suggest that blocking NE activity would abrogate the major protease activity associated with NETs. In addition, the newly identified substrate specificity signatures will guide the design of more specific probes and inhibitors that target NET-associated proteases. | | 24073241
 |
A phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of CHR-3996, an oral class I selective histone deacetylase inhibitor in refractory solid tumors.
Banerji, U; van Doorn, L; Papadatos-Pastos, D; Kristeleit, R; Debnam, P; Tall, M; Stewart, A; Raynaud, F; Garrett, MD; Toal, M; Hooftman, L; De Bono, JS; Verweij, J; Eskens, FA
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
18
2687-94
2012
Show Abstract
This clinical trial investigated the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic (PK), and pharmacodynamic (PD) profile of CHR-3996, a selective class I histone deacetylase inhibitor.CHR-3996 was administered orally once a day. This phase I trial used a 3+3 dose-escalation design. PK profiles were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopic methods and PD studies were conducted using ELISA studying histone H3 acetylation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Thirty-nine patients were treated at dose levels of 5 mg (n = 3), 10 mg (n = 4), 20 mg (n = 3), 40 mg (n = 10), 80 mg (n = 10), 120 mg (n = 4), and 160 mg (n = 5) administered orally once daily. The dose-limiting toxicities seen were thrombocytopenia (160 mg), fatigue (80 and 120 mg), plasma creatinine elevation (80 and 120 mg), and atrial fibrillation (40 mg). The area under the curve was proportional to the administered dose and a maximal plasma concentration of 259 ng/mL at a dose of 40 mg exceeded the concentrations required for antitumor efficacy in preclinical models. Target inhibition measured by quantification of histone acetylation was shown at doses of 10 mg/d and was maximal at 40 mg. A partial response was seen in one patient with metastatic acinar pancreatic carcinoma.Taking the toxicity and PK/PD profile into consideration, the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) is 40 mg/d. At this dose, CHR-3996 has a favorable toxicologic, PK, and PD profile. CHR-3996 has shown preliminary clinical activity and should be evaluated in further clinical trials. | ELISA | 22553374
 |
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae initiates formation of neutrophil extracellular traps.
Juneau, RA; Pang, B; Weimer, KE; Armbruster, CE; Swords, WE
Infection and immunity
79
431-8
2011
Show Abstract
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHI) is a leading cause of otitis media infections, which are often chronic and/or recurrent in nature. NTHI and other bacterial species persist in vivo within biofilms during otitis media and other persistent infections. These biofilms have a significant host component that includes neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). These NETs do not mediate clearance of NTHI, which survives within NET structures by means of specific subpopulations of lipooligosaccharides on the bacterial surface that are determinants of biofilm formation in vitro. In this study, the ability of NTHI and NTHI components to initiate NET formation was examined using an in vitro model system. Both viable and nonviable NTHI strains were shown to promote NET formation, as did preparations of bacterial DNA, outer membrane proteins, and lipooligosaccharide (endotoxin). However, only endotoxin from a parental strain of NTHI exhibited equivalent potency in NET formation to that of NTHI. Additional studies showed that NTHI entrapped within NET structures is resistant to both extracellular killing within NETs and phagocytic killing by incoming neutrophils, due to oligosaccharide moieties within the lipooligosaccharides. Thus, we concluded that NTHI elicits NET formation by means of multiple pathogen-associated molecular patterns (most notably endotoxin) and is highly resistant to killing within NET structures. These data support the conclusion that, for NTHI, formation of NET structures may be a persistence determinant by providing a niche within the middle-ear chamber. | | 20956567
 |
GSK1070916, a potent Aurora B/C kinase inhibitor with broad antitumor activity in tissue culture cells and human tumor xenograft models.
Mary Ann Hardwicke,Catherine A Oleykowski,Ramona Plant,Jamin Wang,Qiaoyin Liao,Katherine Moss,Ken Newlander,Jerry L Adams,Dashyant Dhanak,Jingsong Yang,Zhihong Lai,David Sutton,Denis Patrick
Molecular cancer therapeutics
8
2009
Show Abstract
The protein kinases, Aurora A, B, and C have critical roles in the regulation of mitosis and are frequently overexpressed or amplified in human tumors. GSK1070916, is a novel ATP competitive inhibitor that is highly potent and selective for Aurora B/C kinases. Human tumor cells treated with GSK1070916 show dose-dependent inhibition of phosphorylation on serine 10 of Histone H3, a substrate specific for Aurora B kinase. Moreover, GSK1070916 inhibits the proliferation of tumor cells with EC(50) values of <10 nmol/L in over 100 cell lines spanning a broad range of tumor types. Although GSK1070916 has potent activity against proliferating cells, a dramatic shift in potency is observed in primary, nondividing, normal human vein endothelial cells, consistent with the proposed mechanism. We further determined that treated cells do not arrest in mitosis but instead fail to divide and become polyploid, ultimately leading to apoptosis. GSK1070916 shows dose-dependent inhibition of phosphorylation of an Aurora B-specific substrate in mice and consistent with its broad cellular activity, has antitumor effects in 10 human tumor xenograft models including breast, colon, lung, and two leukemia models. These results show that GSK1070916 is a potent Aurora B/C kinase inhibitor that has the potential for antitumor activity in a wide range of human cancers. | | 19567821
 |
Mitochondrial acetylcarnitine provides acetyl groups for nuclear histone acetylation.
Padma Madiraju,Shri V Pande,Marc Prentki,S R Murthy Madiraju
Epigenetics : official journal of the DNA Methylation Society
4
2009
Show Abstract
Dynamic acetylation and deacetylation of nuclear histones is essential for regulating the access of chromosomal DNA to transcriptional machinery. The source of acetyl-CoA for histone acetylation in mammalian cell nuclei is not clearly known. We show that acetylcarnitine formed in mitochondria, is transported into cytosol by carnitine/acylcarnitine translocase, and then enters nucleus, where it is converted to acetyl-CoA by a nuclear carnitine acetyltransferase and becomes a source of acetyl groups for histone acetylation. Genetic deficiency of the translocase markedly reduced the mitochondrial acetylcarnitine dependent nuclear histone acetylation, indicating the significance of the carnitine-dependent mitochondrial acetyl group contribution to histone acetylation. | | 19755853
 |
GATA-1 modulates the chromatin structure and activity of the chicken alpha-globin 3' enhancer.
Escamilla-Del-Arenal, M; Recillas-Targa, F
Molecular and cellular biology
28
575-86
2008
Show Abstract
Long-distance regulatory elements and local chromatin structure are critical for proper regulation of gene expression. Here we characterize the chromatin conformation of the chicken alpha-globin silencer-enhancer elements located 3' of the domain. We found a characteristic and erythrocyte-specific structure between the previously defined silencer and the enhancer, defined by two nuclease hypersensitive sites, which appear when the enhancer is active during erythroid differentiation. Fine mapping of these sites demonstrates the absence of a positioned nucleosome and the association of GATA-1. Functional analyses of episomal vectors, as well as stably integrated constructs, revealed that GATA-1 plays a major role in defining both the chromatin structure and the enhancer activity. We detected a progressive enrichment of histone acetylation on critical enhancer nuclear factor binding sites, in correlation with the formation of an apparent nucleosome-free region. On the basis of these results, we propose that the local chromatin structure of the chicken alpha-globin enhancer plays a central role in its capacity to differentially regulate alpha-globin gene expression during erythroid differentiation and development. | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) | 17984219
 |