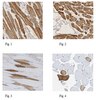
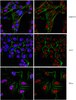
Embryonic MicroRNA-369 Controls Metabolic Splicing Factors and Urges Cellular Reprograming.
Konno, M; Koseki, J; Kawamoto, K; Nishida, N; Matsui, H; Dewi, DL; Ozaki, M; Noguchi, Y; Mimori, K; Gotoh, N; Tanuma, N; Shima, H; Doki, Y; Mori, M; Ishii, H
PloS one
10
e0132789
2015
Show Abstract
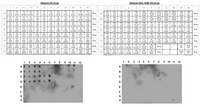
Noncoding microRNAs inhibit translation and lower the transcript stability of coding mRNA, however miR-369 s, in aberrant silencing genomic regions, stabilizes target proteins under cellular stress. We found that in vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells led to chromatin methylation of histone H3K4 at the miR-369 region on chromosome 12qF in mice, which is expressed in embryonic cells and is critical for pluripotency. Proteomic analyses revealed that miR-369 stabilized translation of pyruvate kinase (Pkm2) splicing factors such as HNRNPA2B1. Overexpression of miR-369 stimulated Pkm2 splicing and enhanced induction of cellular reprogramming by induced pluripotent stem cell factors, whereas miR-369 knockdown resulted in suppression. Furthermore, immunoprecipitation analysis showed that the Argonaute complex contained the fragile X mental retardation-related protein 1 and HNRNPA2B1 in a miR-369-depedent manner. Our findings demonstrate a unique role of the embryonic miR-369-HNRNPA2B1 axis in controlling metabolic enzyme function, and suggest a novel pathway linking epigenetic, transcriptional, and metabolic control in cell reprogramming. | | 26176628
 |
Radiation-induced alterations of histone post-translational modification levels in lymphoblastoid cell lines.
Maroschik, B; Gürtler, A; Krämer, A; Rößler, U; Gomolka, M; Hornhardt, S; Mörtl, S; Friedl, AA
Radiation oncology (London, England)
9
15
2014
Show Abstract
Radiation-induced alterations in posttranslational histone modifications (PTMs) may affect the cellular response to radiation damage in the DNA. If not reverted appropriately, altered PTM patterns may cause long-term alterations in gene expression regulation and thus lead to cancer. It is therefore important to characterize radiation-induced alterations in PTM patterns and the factors affecting them.A lymphoblastoid cell line established from a normal donor was used to screen for alterations in methylation levels at H3K4, H3K9, H3K27, and H4K20, as well as acetylation at H3K9, H3K56, H4K5, and H4K16, by quantitative Western Blot analysis at 15 min, 1 h and 24 h after irradiation with 2 Gy and 10 Gy. The variability of alterations in acetylation marks was in addition investigated in a panel of lymphoblastoid cell lines with differing radiosensitivity established from lung cancer patients.The screening procedure demonstrated consistent hypomethylation at H3K4me3 and hypoacetylation at all acetylation marks tested. In the panel of lymphoblastoid cell lines, however, a high degree of inter-individual variability became apparent. Radiosensitive cell lines showed more pronounced and longer lasting H4K16 hypoacetylation than radioresistant lines, which correlates with higher levels of residual γ-H2AX foci after 24 h.So far, the factors affecting extent and duration of radiation-induced histone alterations are poorly defined. The present work hints at a high degree of inter-individual variability and a potential correlation of DNA damage repair capacity and alterations in PTM levels. | Western Blotting | 24406105
 |
ADAM17-mediated CD44 cleavage promotes orasphere formation or stemness and tumorigenesis in HNSCC.
Kamarajan, P; Shin, JM; Qian, X; Matte, B; Zhu, JY; Kapila, YL
Cancer medicine
2
793-802
2013
Show Abstract
CD44, an extracellular matrix (ECM) receptor, has been described as a cancer stem cell marker in multiple cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). HNSCC orasphere formation or stemness was characterized by cleavage of CD44, and thus we hypothesized that this proteolytic processing may be critical to stemness and tumorigenesis. We tested this hypothesis by examining the mechanisms that regulate this process in vitro and in vivo, and by exploring its clinical relevance in human specimens. Sphere assays have been used to evaluate stemness in vitro. Spheres comprised of HNSCC cells or oraspheres and an oral cancer mouse model were used to examine the significance of CD44 cleavage using stable suppression and inhibition approaches. These mechanisms were also examined in HNSCC specimens. Oraspheres exhibited increased levels of CD44 cleavage compared to their adherent counterparts. Given that disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 17 (ADAM17) is a major matrix metalloproteinase known to cleave CD44, we chemically inhibited and stably suppressed ADAM17 expression in HNSCC cells and found that these treatments blocked CD44 cleavage and abrogated orasphere formation. Furthermore, stable suppression of ADAM17 in HNSCC cells also diminished tumorigenesis in an oral cancer mouse model. Consistently, stable suppression of CD44 in HNSCC cells abrogated orasphere formation and inhibited tumorigenesis in vivo. The clinical relevance of these findings was confirmed in matched primary and metastatic human HNSCC specimens, which exhibited increased levels of ADAM17 expression and concomitant CD44 cleavage compared to controls. CD44 cleavage by ADAM17 is critical to orasphere formation or stemness and HNSCC tumorigenesis. | | 24403253
 |
Increased phosphorylation of histone H1 in mouse fibroblasts transformed with oncogenes or constitutively active mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase.
Chadee, D N, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 270: 20098-105 (1995)
1995
Show Abstract
We compared the nucleosomal organization, histone H1 subtypes, and histone H1 phosphorylated isoforms of ras-transformed and parental 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. In agreement with previous studies, we found that ras-transformed mouse fibroblasts have a less condensed chromatin structure than normal fibroblasts. ras-transformed and parental 10T1/2 cells had similar amounts of H1 subtypes, proteins that have a key role in the compaction of chromatin. However, labeling studies with 32P and Western blot experiments with an antiphosphorylated H1 antibody show that interphase ras-transformed cells have higher levels of phosphorylated H1 isoforms than parental cells. G1/S phase-arrested ras-transformed cells had higher amounts of phosphorylated H1 than G1/S phase-arrested parental cells. Mouse fibroblasts transformed with fes, mos, raf, myc, or constitutively active mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase had increased levels of phosphorylated H1. These observations suggest that increased phosphorylation of H1 is one of the consequences of the persistent activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Indirect immunofluorescent studies show that phosphorylated H1b is localized in centers of RNA splicing in the nucleus, suggesting that this modified H1 subtype is complexed to transcriptionally active chromatin. | | 7650028
 |