LTBP-2 Has a Single High-Affinity Binding Site for FGF-2 and Blocks FGF-2-Induced Cell Proliferation.
Menz, C; Parsi, MK; Adams, JR; Sideek, MA; Kopecki, Z; Cowin, AJ; Gibson, MA
PloS one
10
e0135577
2015
Show Abstract
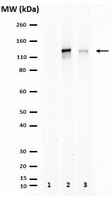
Latent transforming growth factor-beta-1 binding protein-2 (LTBP-2) belongs to the fibrillin-LTBP superfamily of extracellular matrix proteins. LTBPs and fibrillins are involved in the sequestration and storage of latent growth factors, particularly transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), in tissues. Unlike other LTBPs, LTBP-2 does not covalently bind TGF-β, and its molecular functions remain unclear. We are screening LTBP-2 for binding to other growth factors and have found very strong saturable binding to fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) (Kd = 1.1 nM). Using a series of recombinant LTBP-2 fragments a single binding site for FGF-2 was identified in a central region of LTBP-2 consisting of six tandem epidermal growth factor-like (EGF-like) motifs (EGFs 9-14). This region was also shown to contain a heparin/heparan sulphate-binding site. FGF-2 stimulation of fibroblast proliferation was completely negated by the addition of 5-fold molar excess of LTBP-2 to the assay. Confocal microscopy showed strong co-localisation of LTBP-2 and FGF-2 in fibrotic keloid tissue suggesting that the two proteins may interact in vivo. Overall the study indicates that LTBP-2 is a potent inhibitor of FGF-2 that may influence FGF-2 bioactivity during wound repair particularly in fibrotic tissues. | 26263555
 |
Identification of distinct ChAT⁺ neurons and activity-dependent control of postnatal SVZ neurogenesis.
Paez-Gonzalez, P; Asrican, B; Rodriguez, E; Kuo, CT
Nature neuroscience
17
934-42
2014
Show Abstract
Postnatal and adult subventricular zone (SVZ) neurogenesis is believed to be primarily controlled by neural stem cell (NSC)-intrinsic mechanisms, interacting with extracellular and niche-driven cues. Although behavioral experiments and disease states have suggested possibilities for higher level inputs, it is unknown whether neural activity patterns from discrete circuits can directly regulate SVZ neurogenesis. We identified a previously unknown population of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)(+) neurons residing in the rodent SVZ neurogenic niche. These neurons showed morphological and functional differences from neighboring striatal counterparts and released acetylcholine locally in an activity-dependent fashion. Optogenetic inhibition and stimulation of subependymal ChAT(+) neurons in vivo indicated that they were necessary and sufficient to control neurogenic proliferation. Furthermore, whole-cell recordings and biochemical experiments revealed direct SVZ NSC responses to local acetylcholine release, synergizing with fibroblast growth factor receptor activation to increase neuroblast production. These results reveal an unknown gateway connecting SVZ neurogenesis to neuronal activity-dependent control and suggest possibilities for modulating neuroregenerative capacities in health and disease. | 24880216
 |