Differential regulation of apical-basolateral dendrite outgrowth by activity in hippocampal neurons.
Yuan, Y; Seong, E; Yuan, L; Singh, D; Arikkath, J
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience
9
314
2015
Show Abstract
Hippocampal pyramidal neurons have characteristic dendrite asymmetry, characterized by structurally and functionally distinct apical and basolateral dendrites. The ability of the neuron to generate and maintain dendrite asymmetry is vital, since synaptic inputs received are critically dependent on dendrite architecture. Little is known about the role of neuronal activity in guiding maintenance of dendrite asymmetry. Our data indicate that dendrite asymmetry is established and maintained early during development. Further, our results indicate that cell intrinsic and global alterations of neuronal activity have differential effects on net extension of apical and basolateral dendrites. Thus, apical and basolateral dendrite extension may be independently regulated by cell intrinsic and network neuronal activity during development, suggesting that individual dendrites may have autonomous control over net extension. We propose that regulated individual dendrite extension in response to cell intrinsic and neuronal network activity may allow temporal control of synapse specificity in the developing hippocampus. | | 26321915
 |
Prepuberal stimulation of 5-HT7-R by LP-211 in a rat model of hyper-activity and attention-deficit: permanent effects on attention, brain amino acids and synaptic markers in the fronto-striatal interface.
Ruocco, LA; Treno, C; Gironi Carnevale, UA; Arra, C; Boatto, G; Nieddu, M; Pagano, C; Illiano, P; Barbato, F; Tino, A; Carboni, E; Laviola, G; Lacivita, E; Leopoldo, M; Adriani, W; Sadile, AG
PloS one
9
e83003
2014
Show Abstract
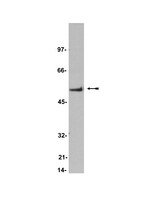
The cross-talk at the prefronto-striatal interface involves excitatory amino acids, different receptors, transducers and modulators. We investigated long-term effects of a prepuberal, subchronic 5-HT7-R agonist (LP-211) on adult behaviour, amino acids and synaptic markers in a model for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Naples High Excitability rats (NHE) and their Random Bred controls (NRB) were daily treated with LP-211 in the 5th and 6th postnatal week. One month after treatment, these rats were tested for indices of activity, non selective (NSA), selective spatial attention (SSA) and emotionality. The quantity of L-Glutamate (L-Glu), L-Aspartate (L-Asp) and L-Leucine (L-Leu), dopamine transporter (DAT), NMDAR1 subunit and CAMKIIα, were assessed in prefrontal cortex (PFC), dorsal (DS) and ventral striatum (VS), for their role in synaptic transmission, neural plasticity and information processing. Prepuberal LP-211 (at lower dose) reduced horizontal activity and (at higher dose) increased SSA, only for NHE but not in NRB rats. Prepuberal LP-211 increased, in NHE rats, L-Glu in the PFC and L-Asp in the VS (at 0.250 mg/kg dose), whereas (at 0.125 mg/kg dose) it decreased L-Glu and L-Asp in the DS. The L-Glu was decreased, at 0.125 mg/kg, only in the VS of NRB rats. The DAT levels were decreased with the 0.125 mg/kg dose (in the PFC), and increased with the 0.250 mg/kg dose (in the VS), significantly for NHE rats. The basal NMDAR1 level was higher in the PFC of NHE than NRB rats; LP-211 treatment (at 0.125 mg/kg dose) decreased NMDAR1 in the VS of NRB rats. This study represents a starting point about the impact of developmental 5-HT7-R activation on neuro-physiology of attentive processes, executive functions and their neural substrates. | Western Blotting | 24709857
 |
Adeno-associated viral serotypes produce differing titers and differentially transduce neurons within the rat basal and lateral amygdala.
Holehonnur, R; Luong, JA; Chaturvedi, D; Ho, A; Lella, SK; Hosek, MP; Ploski, JE
BMC neuroscience
15
28
2014
Show Abstract
In recent years, there has been an increased interest in using recombinant adeno-associated viruses (AAV) to make localized genetic manipulations within the rodent brain. Differing serotypes of AAV possess divergent capsid protein sequences and these variations greatly influence each serotype's ability to transduce particular cell types and brain regions. We therefore aimed to determine the AAV serotype that is optimal for targeting neurons within the Basal and Lateral Amygdala (BLA) since the transduction efficiency of AAV has not been previously examined within the BLA. This region is desirable to genetically manipulate due to its role in emotion, learning & memory, and numerous psychiatric disorders. We accomplished this by screening 9 different AAV serotypes (AAV2/1, AAV2/2, AAV2/5, AAV2/7, AAV2/8, AAV2/9, AAV2/rh10, AAV2/DJ and AAV2/DJ8) designed to express red fluorescent protein (RFP) under the regulation of an alpha Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II promoter (αCaMKII).We determined that these serotypes produce differing amounts of virus under standard laboratory production. Notably AAV2/2 consistently produced the lowest titers compared to the other serotypes examined. These nine serotypes were bilaterally infused into the rat BLA at the highest titers achieved for each serotype and at a normalized titer of 7.8E + 11 GC/ml. Twenty one days following viral infusion the degree of transduction was quantitated throughout the amygdala. These viruses exhibited differential transduction of neurons within the BLA. AAV2/7 exhibited a trend toward having the highest efficiency of transduction and AAV2/5 exhibited significantly lower transduction efficiency as compared to the serotypes examined. AAV2/5's decreased ability to transduce BLA neurons correlates with its significantly different capsid protein sequences as compared to the other serotypes examined.For laboratories producing their own recombinant adeno-associated viruses, the use of AAV2/2 is likely less desirable since AAV2/2 produces significantly lower titers than many other serotypes of AAV. Numerous AAV serotypes appear to efficiently transduce BLA neurons, with the exception of AAV2/5. Taking into consideration the ability of certain serotypes to achieve high titers and transduce BLA neurons well, in our hands AAV2/DJ8 and AAV2/9 appear to be ideal serotypes to use when targeting neurons within the BLA. | | 24533621
 |
Time-dependent activation of MAPK/Erk1/2 and Akt/GSK3 cascades: modulation by agomelatine.
Musazzi, L; Seguini, M; Mallei, A; Treccani, G; Pelizzari, M; Tornese, P; Racagni, G; Tardito, D
BMC neuroscience
15
119
2014
Show Abstract
The novel antidepressant agomelatine, a melatonergic MT1/MT2 agonist combined with 5-HT2c serotonin antagonist properties, showed antidepressant action in preclinical and clinical studies. There is a general agreement that the therapeutic action of antidepressants needs the activation of slow-onset adaptations in downstream signalling pathways finally regulating neuroplasticity. In the last several years, particular attention was given to cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB)-related pathways, since it was shown that chronic antidepressants increase CREB phosphorylation and transcriptional activity, through the activation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent (CaM) and mitogen activated protein kinase cascades (MAPK/Erk1/2). Aim of this work was to analyse possible effects of chronic agomelatine on time-dependent changes of different intracellular signalling pathways in hippocampus and prefrontal/frontal cortex of male rats. To this end, measurements were performed 1 h or 16 h after the last agomelatine or vehicle injection.We have found that in naïve rats chronic agomelatine, contrary to traditional antidepressants, did not increase CREB phosphorylation, but modulates the time-dependent regulation of MAPK/Erk1/2 and Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) pathways.Our results suggest that the intracellular molecular mechanisms modulated by chronic agomelatine may be partly different from those of traditional antidepressants and involve the time-dependent regulation of MAPK/Erk1/2 and Akt/GSK-3 signalling pathways. This could exert a role in the antidepressant efficacy of the drug. | Western Blotting | 25332063
 |
Behavioral and structural responses to chronic cocaine require a feedforward loop involving ΔFosB and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the nucleus accumbens shell.
Robison, AJ; Vialou, V; Mazei-Robison, M; Feng, J; Kourrich, S; Collins, M; Wee, S; Koob, G; Turecki, G; Neve, R; Thomas, M; Nestler, EJ
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
33
4295-307
2013
Show Abstract
The transcription factor ΔFosB and the brain-enriched calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKIIα) are induced in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) by chronic exposure to cocaine or other psychostimulant drugs of abuse, in which the two proteins mediate sensitized drug responses. Although ΔFosB and CaMKIIα both regulate AMPA glutamate receptor expression and function in NAc, dendritic spine formation on NAc medium spiny neurons (MSNs), and locomotor sensitization to cocaine, no direct link between these molecules has to date been explored. Here, we demonstrate that ΔFosB is phosphorylated by CaMKIIα at the protein-stabilizing Ser27 and that CaMKII is required for the cocaine-mediated accumulation of ΔFosB in rat NAc. Conversely, we show that ΔFosB is both necessary and sufficient for cocaine induction of CaMKIIα gene expression in vivo, an effect selective for D1-type MSNs in the NAc shell subregion. Furthermore, induction of dendritic spines on NAc MSNs and increased behavioral responsiveness to cocaine after NAc overexpression of ΔFosB are both CaMKII dependent. Importantly, we demonstrate for the first time induction of ΔFosB and CaMKII in the NAc of human cocaine addicts, suggesting possible targets for future therapeutic intervention. These data establish that ΔFosB and CaMKII engage in a cell-type- and brain-region-specific positive feedforward loop as a key mechanism for regulating the reward circuitry of the brain in response to chronic cocaine. | | 23467346
 |
Lmo4 in the basolateral complex of the amygdala modulates fear learning.
Maiya, R; Kharazia, V; Lasek, AW; Heberlein, U
PloS one
7
e34559
2012
Show Abstract
Pavlovian fear conditioning is an associative learning paradigm in which mice learn to associate a neutral conditioned stimulus with an aversive unconditioned stimulus. In this study, we demonstrate a novel role for the transcriptional regulator Lmo4 in fear learning. LMO4 is predominantly expressed in pyramidal projection neurons of the basolateral complex of the amygdala (BLC). Mice heterozygous for a genetrap insertion in the Lmo4 locus (Lmo4gt/+), which express 50% less Lmo4 than their wild type (WT) counterparts display enhanced freezing to both the context and the cue in which they received the aversive stimulus. Small-hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of Lmo4 in the BLC, but not the dentate gyrus region of the hippocampus recapitulated this enhanced conditioning phenotype, suggesting an adult- and brain region-specific role for Lmo4 in fear learning. Immunohistochemical analyses revealed an increase in the number of c-Fos positive puncta in the BLC of Lmo4gt/+ mice in comparison to their WT counterparts after fear conditioning. Lastly, we measured anxiety-like behavior in Lmo4gt/+ mice and in mice with BLC-specific downregulation of Lmo4 using the elevated plus maze, open field, and light/dark box tests. Global or BLC-specific knockdown of Lmo4 did not significantly affect anxiety-like behavior. These results suggest a selective role for LMO4 in the BLC in modulating learned but not unlearned fear. | | 22509321
 |
Involvement of the insular cortex in regulating glucocorticoid effects on memory consolidation of inhibitory avoidance training.
Fornari, RV; Wichmann, R; Atucha, E; Desprez, T; Eggens-Meijer, E; Roozendaal, B
Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience
6
10
2012
Show Abstract
Glucocorticoids are known to enhance the consolidation of memory of emotionally arousing experiences by acting upon a network of interconnected brain regions. Although animal studies typically do not consider the insular cortex (IC) to be part of this network, the present findings indicate that the IC is importantly involved in regulating glucocorticoid effects on memory consolidation of emotionally arousing inhibitory avoidance training. The specific glucocorticoid receptor (GR) agonist RU 28362 (3 or 10 ng in 0.5 μl) infused bilaterally into the IC of male Sprague-Dawley rats immediately after one-trial inhibitory avoidance training dose-dependently enhanced 48 h retention performance. Moreover, training on the inhibitory avoidance task increased neuronal activity of the IC, as assessed by an increased number of cells expressing immunoreactivity for phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (pERK1/2). However, systemic administration of a memory-enhancing dose of corticosterone (1 mg/kg) after inhibitory avoidance training rapidly reduced the number of pERK1/2-positive cells in the IC, suggesting that glucocorticoid administration reduces overall neuronal activity of the IC. To investigate which components of the inhibitory avoidance training experience were influenced by the intra-IC glucocorticoid administration, in the last experiment rats were trained on a modified inhibitory avoidance task in which context exposure and footshock training occur on two sequential days. RU 28362 administration into the IC enhanced later retention when infused immediately after either the context or footshock training. Thus, these findings indicate that the IC mediates glucocorticoid effects on the consolidation of memory of different components of inhibitory avoidance training and suggest that the IC might be an important element of the rodent brain network involved in emotional regulation of learning and memory. | | 22435055
 |
Comparative study of human and mouse postsynaptic proteomes finds high compositional conservation and abundance differences for key synaptic proteins.
Bayés, A; Collins, MO; Croning, MD; van de Lagemaat, LN; Choudhary, JS; Grant, SG
PloS one
7
e46683
2012
Show Abstract
Direct comparison of protein components from human and mouse excitatory synapses is important for determining the suitability of mice as models of human brain disease and to understand the evolution of the mammalian brain. The postsynaptic density is a highly complex set of proteins organized into molecular networks that play a central role in behavior and disease. We report the first direct comparison of the proteome of triplicate isolates of mouse and human cortical postsynaptic densities. The mouse postsynaptic density comprised 1556 proteins and the human one 1461. A large compositional overlap was observed; more than 70% of human postsynaptic density proteins were also observed in the mouse postsynaptic density. Quantitative analysis of postsynaptic density components in both species indicates a broadly similar profile of abundance but also shows that there is higher abundance variation between species than within species. Well known components of this synaptic structure are generally more abundant in the mouse postsynaptic density. Significant inter-species abundance differences exist in some families of key postsynaptic density proteins including glutamatergic neurotransmitter receptors and adaptor proteins. Furthermore, we have identified a closely interacting set of molecules enriched in the human postsynaptic density that could be involved in dendrite and spine structural plasticity. Understanding synapse proteome diversity within and between species will be important to further our understanding of brain complexity and disease. | | 23071613
 |
Glucocorticoid receptors recruit the CaMKIIα-BDNF-CREB pathways to mediate memory consolidation.
Chen, DY; Bambah-Mukku, D; Pollonini, G; Alberini, CM
Nature neuroscience
15
1707-14
2012
Show Abstract
Emotionally important events are well remembered. Although memories of emotional experiences are known to be mediated and modulated by stress hormones such as glucocorticoids, little is known about the underlying molecular mechanisms. We found that the hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors that are critically engaged during the formation of long-term inhibitory avoidance memory in rats were coupled to the activation of CaMKIIα, TrkB, ERK, Akt, PLCγ and CREB, as well as a to a substantial induction of Arc and synaptic GluA1. Most of these changes, which are initiated by a nongenomic effect of glucocorticoid receptors, were also downstream of the activation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Hippocampal administration of BDNF, but not of other neurotrophins, selectively rescued both the amnesia and the molecular impairments produced by glucocorticoid receptor inhibition. Thus, glucocorticoid receptors mediate long-term memory formation by recruiting the CaMKIIα-BDNF-CREB-dependent neural plasticity pathways. | | 23160045
 |
Intermittent noxious stimulation following spinal cord contusion injury impairs locomotor recovery and reduces spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor-tropomyosin-receptor kinase signaling in adult rats.
Garraway, SM; Turtle, JD; Huie, JR; Lee, KH; Hook, MA; Woller, SA; Grau, JW
Neuroscience
199
86-102
2011
Show Abstract
Intermittent nociceptive stimulation following a complete transection or contused spinal cord injury (SCI) has been shown to exert several short- and long-lasting negative consequences. These include maladaptive spinal plasticity, enhanced mechanical allodynia, and impaired functional recovery of locomotor and bladder functions. The neurotrophin, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has been shown to play an important role in adaptive plasticity and also to restore functions following SCI. This suggests that the negative behavioral effects of shock are most likely related to corresponding changes in BDNF spinal levels. In this study, we investigated the cellular effects of nociceptive stimulation in contused adult rats focusing on BDNF, its receptor, tropomyosin-receptor kinase (TrkB), and the subsequent downstream signaling system. The goal was to determine whether the behavioral effect of stimulation is associated with concomitant cellular changes induced during the initial post-injury period. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting were used to assess changes in the mRNA and/or protein levels of BDNF, TrkB, and the downstream signaling proteins calcium-calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) and extracellular related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) at 1 h, 24 h, and 7 days following administration of intermittent noxious shock to the tail of contused subjects. In addition, recovery of locomotor function (Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan [BBB] score) was assessed daily for the first week after injury. The results showed that, although nociceptive stimulation failed to induce any changes in gene expression at 1 h, it significantly reduced the expression of BDNF, TrkB, ERK2, and CaMKII at 24 h. In general, changes in gene expression were spatially localized to the dorsal spinal cord. In addition, locomotor recovery was impaired by shock. Evidence is also provided suggesting that shock engages a neuronal circuitry without having any negative effects on neuronal survival at 24 h. These results suggest that nociceptive activity following SCI decreases BDNF and TrkB levels, which may significantly contribute to diminished functional recovery. | Immunohistochemistry | 22027236
 |