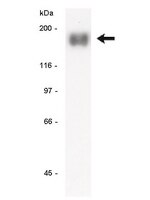
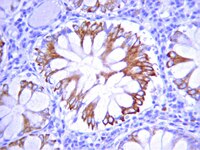
Efficacy of aerosol therapy of lung cancer correlates with EGFR paralysis induced by AvidinOX-anchored biotinylated Cetuximab.
De Santis, R; Rosi, A; Anastasi, AM; Chiapparino, C; Albertoni, C; Leoni, B; Pelliccia, A; Santapaola, D; Carollo, V; Marra, E; Aurisicchio, L; Arseni, B; Pacello, ML; Palmieri, G; Battella, S; Petronzelli, F; Milazzo, FM
Oncotarget
5
9239-55
2014
Show Abstract
Lung cancer, as well as lung metastases from distal primary tumors, could benefit from aerosol treatment. Unfortunately, because of lung physiology, clearance of nebulized drugs is fast, paralleled by unwanted systemic exposure. Here we report that nebulized AvidinOX can act as an artificial receptor for biotinylated drugs. In nude and SCID mice with advanced human KRAS-mutated A549 metastatic lung cancer, pre-nebulization with AvidinOX enables biotinylated Cetuximab to control tumor growth at a dose lower than 1/25,000 the intravenous effective dose. This result correlates with a striking, specific and unpredictable effect of AvidinOX-anchored biotinylated Cetuximab, as well as Panitumumab, observed on a panel of tumor cell lines, leading to inhibition of dimerization and signalling, blockade of endocytosis, induction of massive lysosomal degradation and abrogation of nuclear translocation of EGFR. Excellent tolerability, together with availability of pharmaceutical-grade AvidinOX and antibodies, will allow rapid clinical translation of the proposed therapy. | Western Blotting | 25238453
 |
Glioma surgical aspirate: a viable source of tumor tissue for experimental research.
Day, BW; Stringer, BW; Wilson, J; Jeffree, RL; Jamieson, PR; Ensbey, KS; Bruce, ZC; Inglis, P; Allan, S; Winter, C; Tollesson, G; Campbell, S; Lucas, P; Findlay, W; Kadrian, D; Johnson, D; Robertson, T; Johns, TG; Bartlett, PF; Osborne, GW; Boyd, AW
Cancers
5
357-71
2013
Show Abstract
Brain cancer research has been hampered by a paucity of viable clinical tissue of sufficient quality and quantity for experimental research. This has driven researchers to rely heavily on long term cultured cells which no longer represent the cancers from which they were derived. Resection of brain tumors, particularly at the interface between normal and tumorigenic tissue, can be carried out using an ultrasonic surgical aspirator (CUSA) that deposits liquid (blood and irrigation fluid) and resected tissue into a sterile bottle for disposal. To determine the utility of CUSA-derived glioma tissue for experimental research, we collected 48 CUSA specimen bottles from glioma patients and analyzed both the solid tissue fragments and dissociated tumor cells suspended in the liquid waste fraction. We investigated if these fractions would be useful for analyzing tumor heterogeneity, using IHC and multi-parameter flow cytometry; we also assessed culture generation and orthotopic xenograft potential. Both cell sources proved to be an abundant, highly viable source of live tumor cells for cytometric analysis, animal studies and in-vitro studies. Our findings demonstrate that CUSA tissue represents an abundant viable source to conduct experimental research and to carry out diagnostic analyses by flow cytometry or other molecular diagnostic procedures. | Immunohistochemistry | 24216981
 |
Microbead arrays for the analysis of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase activation and dimerization in breast cancer cells.
Khan IH, Zhao J, Ghosh P, Ziman M, Sweeney C, Kung HJ, Luciw PA
Assay Drug Dev Technol
8
27-36.
2010
Show Abstract
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in the ErbB family (EGFR, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4) are implicated in a variety of human malignancies. Accordingly, determination of both expression and activation (dimerization/heterodimerization and phosphorylation) of ErbB proteins is critical in defining their functional role in cancer. Efficient and comprehensive methods to study molecular functions of ErbB family of RTKs are needed not only for improvements in diagnostics but also for early screening of targeted drugs (eg, small molecule inhibitors and therapeutic antibodies). We report development of 3 multiplex microbead immunoassays for simultaneous detection of expression, protein-protein interactions, and phosphorylation of these RTKs. These novel multiplex immunoassays were used to study ErbB RTKs under different cell activation conditions in 2 breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-453 and MDA-MB-468) and an epidermoid cancer cell line (A431). The results were confirmed by immunoprecipitation/western blot. Importantly, the multiplex immunoassay facilitated time-course studies in these cell lines after cell activation with EGF and neuregulin, revealing the kinetics of phosphorylation of the ErbB family RTKs. This study demonstrates the utility of the Luminex(R) multiplex system as an efficient and comprehensive approach to study different aspects of molecular roles of these RTKs. Importantly, the study provides proof-of-concept for the utility of the multiplex microbead immunoassay approach for potential use in efficient, robust, and rapid screening of drugs, particularly those targeting functional aspects of these potent signaling molecules. In addition, the assays described here may be useful for cancer diagnostics and monitoring efficacy of therapy targeting the ErbB family of RTKs. | | 20035613
 |
RNA interference screen identifies Usp18 as a regulator of epidermal growth factor receptor synthesis.
Duex, JE; Sorkin, A
Molecular biology of the cell
20
1833-44
2009
Show Abstract
Elevated expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) contributes to the progression of many types of cancer. Therefore, we developed a high-throughput screen to identify proteins that regulate the levels of EGFR in squamous cell carcinoma. Knocking down various ubiquitination-related genes with small interfering RNAs led to the identification of several novel genes involved in this process. One of these genes, Usp18, is a member of the ubiquitin-specific protease family. We found that knockdown of Usp18 in several cell lines reduced expression levels of EGFR by 50-80%, whereas the levels of other receptor tyrosine kinases remained unchanged. Overexpression of Usp18 elevated EGFR levels in a manner requiring the catalytic cysteine of Usp18. Analysis of metabolically radiolabeled cells showed that the rate of EGFR protein synthesis was reduced up to fourfold in the absence of Usp18. Interestingly, this dramatic reduction occurred despite no change in the levels of EGFR mRNA. This suggests that depletion of Usp18 inhibited EGFR mRNA translation. In fact, this inhibition required the presence of native 5' and 3' untranslated region sequences on EGFR mRNA. Together, our data provide evidence for the novel mechanism of EGFR regulation at the translational step of receptor synthesis. Full Text Article | | 19158387
 |
Enhanced estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, ERBB2, and MAPK signal transduction pathways operate during the adaptation of MCF-7 cells to long term estrogen deprivation.
Martin, Lesley-Ann, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 278: 30458-68 (2003)
2003
Show Abstract
The mechanisms involved in resistance to estrogen deprivation are of major importance for optimal patient therapy and the development of new drugs. Long term culture of MCF-7 cells in estrogen (E2)-depleted medium (long term estrogen deprivation; LTED) results in hypersensitivity to E2 coinciding with elevated levels of estrogen receptor (ER) alpha phosphorylated on Ser118 and MAPK, together with several of its downstream targets associated previously with ERalpha phosphorylation. Our data suggest elevated MAPK activity results from enhanced ERBB2 expression in the LTED cells versus the wild-type (wt), and treatment with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 revealed increased sensitivity in both transcription and proliferation assays. Similarly the MEK inhibitor U0126 decreased transcription and proliferation in the LTED cells and reduced their sensitivity to the proliferative effects of E2, while having no effect on the wt. However, the complete suppression of MAPK activity in the LTED cells did not inhibit ERalpha Ser118 phosphorylation suggesting that ER activity remained ligand-dependant. The LTED cells also expressed elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor-1R, and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity with LY294002 reduced basal ERalpha transactivation by 70% in the LTED cells compared with the wt. However, LY294002 had no effect on ERalpha Ser118 phosphorylation. These data suggest that although elevated levels of MAPK occur during LTED and influence the phenotype, this is unlikely to be the sole pathway operating to achieve adaptation. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 12775708
 |
Aging-related attenuation of EGF receptor signaling is mediated in part by increased protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.
Kien T Tran, S Diana Rusu, Latha Satish, Alan Wells
Experimental cell research
289
359-67
2003
Show Abstract
As fibroblasts near senescence, their responsiveness to external signals diminishes. This well-documented phenomenon likely underlies physiological deterioration and limited tissue regeneration in aging individuals. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms would provide opportunities to ameliorate these situations. A key stimulus for human dermal fibroblasts are ligands for the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). We have shown earlier that EGFR expression decreases by about half in near senescent fibroblasts (Shiraha et al., 2000, J. Biol. Chem. 275 (25), 19343-19351). However, as the cell responses are nearly absent near senescence, other aging-related signal attenuation changes must also occur. Herein, we show that EGFR signaling as determined by receptor autophosphorylation is diminished over 80%, with a corresponding decrease in the phosphorylation of the immediate postreceptor adaptor Shc. Interestingly, we found that this was due at least in part to increased dephosphorylation of EGFR. The global cell phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity increased some threefold in near senescent cells. An initial survey of EGFR-associated protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPases) showed that SHP-1 (PTPIC, HCP, SHPTP-1) and PTPIB levels are increased in parallel in these cells. Concomitantly, we also discovered an increase in expression of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (RPTPalpha). Last, inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases by sodium orthovanadate in near senescent cells resulted in increased EGFR phosphorylation. These data support a model in which, near senescence, dermal fibroblasts become resistant to EGFR-mediated stimuli by a combination of receptor downregulation and increased signal attenuation. | | 14499637
 |
Endocytosis of epidermal growth factor receptor regulated by Grb2-mediated recruitment of the Rab5 GTPase-activating protein RN-tre.
Martinu, L; Santiago-Walker, A; Qi, H; Chou, MM
The Journal of biological chemistry
277
50996-1002
2002
Show Abstract
The Grb2 adaptor protein is best known for its role in signaling to the small GTPase p21(ras), mediated through its interaction with the SOS guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Here, we demonstrate that Grb2 also signals to Rab5, a small GTPase that plays a key role in early endocytic trafficking. Grb2 functions through association with RN-tre, a GTPase-activating protein for Rab5. Grb2 and RN-tre associate both in vitro and in vivo, with interaction mediated by both SH3 domains of Grb2 and extended proline-rich sequences in RN-tre. Association between Grb2 and RN-tre is constitutive and occurs independently of Eps8, a previously identified binding partner of RN-tre. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates recruitment of RN-tre to the EGF receptor (EGFR) in a Grb2-dependent manner. Grb2 and the EGFR are internalized and co-localized in endocytic vesicles in response to EGF. Overexpression of RN-tre blocks the internalization of both proteins, consistent with its function as a negative regulator of Rab5 and endocytosis. Strikingly, RN-tre does not block EGF-induced internalization of a Grb2 mutant deficient in RN-tre binding. These results 1) suggest that the ability of RN-tre to inhibit internalization of the EGFR requires Grb2-mediated binding to the receptor and 2) identify Grb2 as a critical regulator of Rab5 and EGFR endocytosis. | Immunofluorescence | 12399475
 |
Epidermal growth factor receptor induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of Ras signaling.
T Högnason, S Chatterjee, T Vartanian, R R Ratan, K M Ernewein, A A Habib, T Högnason, S Chatterjee, T Vartanian, R R Ratan, K M Ernewein, A A Habib
FEBS letters
491
9-15
2001
Show Abstract
Previous studies have shown that certain tumor cell lines which naturally express high levels of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) undergo apoptosis when exposed to epidermal growth factor. Whether this phenomenon is a direct result of receptor overexpression or some other genetic alteration renders these cells sensitive to apoptosis is yet to be established. We show that experimentally increasing the level of EGFR expression predictably leads to apoptosis in a variety of cell types which requires an active tyrosine kinase but not EGFR autophosphorylation sites. Expression of a dominant negative Ras mutant in EGFR overexpressing cells results in a significant potentiation of EGFR induced apoptosis suggesting that Ras activation is a key survival signal generated by the EGFR. We propose that potentiation of EGFR induced apoptosis by dominant negative Ras results, at least in part, by a block of Akt activation. | | 11226409
 |
Peroxynitrite targets the epidermal growth factor receptor, Raf-1, and MEK independently to activate MAPK.
Zhang, P, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 275: 22479-86 (2000)
2000
Show Abstract
Activation of ERK-1 and -2 by H(2)O(2) in a variety of cell types requires epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) phosphorylation. In this study, we investigated the activation of ERK by ONOO(-) in cultured rat lung myofibroblasts. Western blot analysis using anti-phospho-ERK antibodies along with an ERK kinase assay using the phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein (PHAS-1) substrate demonstrated that ERK activation peaked within 15 min after ONOO(-) treatment and was maximally activated with 100 micrometer ONOO(-). Activation of ERK by ONOO(-) and H(2)O(2) was blocked by the antioxidant N-acetyl-l-cysteine. Catalase blocked ERK activation by H(2)O(2), but not by ONOO(-), demonstrating that the effect of ONOO(-) was not due to the generation of H(2)O(2). Both H(2)O(2) and ONOO(-) induced phosphorylation of EGFR in Western blot experiments using an anti-phospho-EGFR antibody. However, the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 abolished ERK activation by H(2)O(2), but not by ONOO(-). Both H(2)O(2) and ONOO(-) activated Raf-1. However, the Raf inhibitor forskolin blocked ERK activation by H(2)O(2), but not by ONOO(-). The MEK inhibitor PD98059 inhibited ERK activation by both H(2)O(2) and ONOO(-). Moreover, ONOO(-) or H(2)O(2) caused a cytotoxic response of myofibroblasts that was prevented by preincubation with PD98059. In a cell-free kinase assay, ONOO(-) (but not H(2)O(2)) induced autophosphorylation and nitration of a glutathione S-transferase-MEK-1 fusion protein. Collectively, these data indicate that ONOO(-) activates EGFR and Raf-1, but these signaling intermediates are not required for ONOO(-)-induced ERK activation. However, MEK-1 activation is required for ONOO(-)-induced ERK activation in myofibroblasts. In contrast, H(2)O(2)-induced ERK activation is dependent on EGFR activation, which then leads to downstream Raf-1 and MEK-1 activation. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 10801894
 |
A differential requirement for the COOH-terminal region of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor in amphiregulin and EGF mitogenic signaling
Wong, L., et al
J Biol Chem, 274:8900-9 (1999)
1999
| Immunoblotting (Western) | 10085134
 |