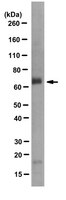
The PtdIns3P phosphatase myotubularin is a cytoplasmic protein that also localizes to Rac1-inducible plasma membrane ruffles.
Laporte, Jocelyn, et al.
J. Cell. Sci., 115: 3105-17 (2002)
2002
Show Abstract
Myotubularin, the phosphatase mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy, was shown to dephosphorylate phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate (PtdIns3P) and was also reported to interact with nuclear transcriptional regulators from the trithorax family. We have characterized a panel of specific antibodies and investigated the subcellular localization of myotubularin. Myotubularin is not detected in the nucleus, and localizes mostly as a dense cytoplasmic network. Overexpression of myotubularin does not detectably affect vesicle trafficking in the mammalian cells investigated, in contrast to previous observations in yeast models. Both mutation of a key aspartate residue of myotubularin and dominant activation of Rac1 GTPase lead to the recruitment of myotubularin to specific plasma membrane domains. Localization to Rac1-induced ruffles is dependent on the presence of a domain highly conserved in the myotubularin family (that we named RID). We thus propose that myotubularin may dephosphorylate a subpool of PtdIns3P (or another related substrate) at the plasma membrane. | 12118066
 |
Muscle-specific alternative splicing of myotubularin-related 1 gene is impaired in DM1 muscle cells.
Buj-Bello, Anna, et al.
Hum. Mol. Genet., 11: 2297-307 (2002)
2002
Show Abstract
The myotubularin-related 1 (MTMR1) gene belongs to a highly conserved family of eucaryotic phosphatases, with at least 11 members in humans. The founder member of this gene family, MTM1, is mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy, a severe congenital disorder that affects skeletal muscle, and codes for myotubularin, a specific phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PI(3)P] phosphatase. MTM1 and MTMR1 are adjacent on the X chromosome, and the corresponding proteins share 59% sequence identity. In the present study, we investigated the putative role of MTMR1 in myogenesis by analysing its expression pattern in muscle cells during differentiation and in skeletal muscle throughout development. We have identified three novel coding exons in the MTMR1 intron 2 that are conserved between mouse and human, are alternatively spliced, and give rise to six mRNA isoforms. One of the transcripts is muscle-specific and is induced during myogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, and represents the major isoform in adult skeletal muscle. We show that the two main MTMR1 protein muscular isoforms, like myotubularin, efficiently dephosphorylate PI(3)P in vitro. We have also analysed whether MTMR1 alternative splicing is affected in skeletal muscle cells derived from patients with congenital myotonic dystrophy (cDM1), in which mRNA splicing disturbances of specific genes are thought to constitute an important pathogenic mechanism. We found a striking reduction in the level of the muscle-specific isoform and the appearance of an abnormal MTMR1 transcript in differentiated cDM1 muscle cells in culture and in skeletal muscle from cDM1 patients. Our results suggest that MTMR1 plays a role in muscle formation and represents a novel target for abnormal mRNA splicing in myotonic dystrophy. | 12217958
 |