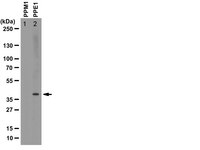
Altered protein phosphatase 2A methylation and Tau phosphorylation in the young and aged brain of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) deficient mice.
Sontag, JM; Wasek, B; Taleski, G; Smith, J; Arning, E; Sontag, E; Bottiglieri, T
Frontiers in aging neuroscience
6
214
2014
Show Abstract
Common functional polymorphisms in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene, a key enzyme in folate and homocysteine metabolism, influence risk for a variety of complex disorders, including developmental, vascular, and neurological diseases. MTHFR deficiency is associated with elevation of homocysteine levels and alterations in the methylation cycle. Here, using young and aged Mthfr knockout mouse models, we show that mild MTHFR deficiency can lead to brain-region specific impairment of the methylation of Ser/Thr protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). Relative to wild-type controls, decreased expression levels of PP2A and leucine carboxyl methyltransferase (LCMT1) were primarily observed in the hippocampus and cerebellum, and to a lesser extent in the cortex of young null Mthfr (-/-) and aged heterozygous Mthfr (+/-) mice. A marked down regulation of LCMT1 correlated with the loss of PP2A/Bα holoenzymes. Dietary folate deficiency significantly decreased LCMT1, methylated PP2A and PP2A/Bα levels in all brain regions examined from aged Mthfr (+/+) mice, and further exacerbated the regional effects of MTHFR deficiency in aged Mthfr (+/-) mice. In turn, the down regulation of PP2A/Bα was associated with enhanced phosphorylation of Tau, a neuropathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Our findings identify hypomethylation of PP2A enzymes, which are major CNS phosphatases, as a novel mechanism by which MTHFR deficiency and Mthfr gene-diet interactions could lead to disruption of neuronal homeostasis, and increase the risk for a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders, including age-related diseases like sporadic AD. | Western Blotting | 25202269
 |
Cytoplasmic SET induces tau hyperphosphorylation through a decrease of methylated phosphatase 2A.
Chasseigneaux, S; Clamagirand, C; Huguet, L; Gorisse-Hussonnois, L; Rose, C; Allinquant, B
BMC neuroscience
15
82
2014
Show Abstract
The neuronal cytoplasmic localization of SET, an inhibitor of the phosphatase 2A (PP2A), results in tau hyperphosphorylation in the brains of Alzheimer patients through mechanisms that are still not well defined.We used primary neurons and mouse brain slices to show that SET is translocated to the cytoplasm in a manner independent of both its cleavage and over-expression. The localization of SET in the cytoplasm, either by the translocation of endogenous SET or by internalization of the recombinant full-length SET protein, induced tau hyperphosphorylation. Cytoplasmic recombinant full-length SET in mouse brain slices induced a decrease of PP2A activity through a decrease of methylated PP2A levels. The levels of methylated PP2A were negatively correlated with tau hyperphosphorylation at Ser-202 but not with the abnormal phosphorylation of tau at Ser-422.The presence of full-length SET in the neuronal cytoplasm is sufficient to impair PP2A methylation and activity, leading to tau hyperphosphorylation. In addition, our data suggest that tau hyperphosphorylation is regulated by different mechanisms at distinct sites. The translocation of SET to the neuronal cytoplasm, the low activity of PP2A, and tau hyperphosphorylation are associated in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Our data show a link between the translocation of SET in the cytoplasm and the decrease of methylated PP2A levels leading to a decrease of PP2A activity and tau hyperphosphorylation. This chain of events may contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. | Western Blotting | 24981783
 |
NNMT promotes epigenetic remodeling in cancer by creating a metabolic methylation sink.
Ulanovskaya, OA; Zuhl, AM; Cravatt, BF
Nature chemical biology
9
300-6
2013
Show Abstract
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers, where it contributes to tumorigenesis by a mechanism that is still poorly understood. Here we show using metabolomics that NNMT impairs the methylation potential of cancer cells by consuming methyl units from S-adenosyl methionine to create the stable metabolic product 1-methylnicotinamide. As a result, NNMT-expressing cancer cells have an altered epigenetic state that includes hypomethylated histones and other cancer-related proteins combined with heightened expression of protumorigenic gene products. Our findings thus point to a direct mechanistic link between the deregulation of a metabolic enzyme and widespread changes in the methylation landscape of cancer cells. | Western Blotting | 23455543
 |
Protein phosphatase 2A carboxymethylation and regulatory B subunits differentially regulate mast cell degranulation.
Kranias, Gregory, et al.
Cell. Signal., 22: 1882-90 (2010)
2010
Show Abstract
Asthma is characterised by antigen-mediated mast cell degranulation resulting in secretion of inflammatory mediators. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is a serine/threonine protein phosphatase composed of a catalytic (PP2A-C) subunit together with a core scaffold (PP2A-A) subunit and a variable, regulatory (PP2A-B) subunit. Previous studies utilising pharmacological inhibition of protein phosphatases have suggested a positive regulatory role for PP2A in mast cell degranulation. In support of this we find that a high okadaic acid concentration (1μM) inhibits mast cell degranulation. Strikingly, we now show that a low concentration of okadaic acid (0.1μM) has the opposite effect, resulting in enhanced degranulation. Selective downregulation of the PP2A-Cα subunit by short hairpin RNA also enhanced degranulation of RBL-2H3 mast cells, suggesting that the primary role of PP2A is to negatively regulate degranulation. PP2A-B subunits are responsible for substrate specificity, and carboxymethylation of the PP2A-C subunit alters B subunit binding. We show here that carboxymethylation of PP2A-C is dynamically altered during degranulation and inhibition of methylation decreases degranulation. Moreover downregulation of the PP2A-Bα subunit resulted in decreased MK2 phosphorylation and degranulation, whilst downregulation of the PP2A-B'δ subunit enhanced p38 MAPK phosphorylation and degranulation. Taken together these data show that PP2A is both a positive and negative regulator of mast cell degranulation, and this differential role is regulated by carboxymethylation and specific PP2A-B subunit binding. | | 20688157
 |