ZEB1-associated drug resistance in cancer cells is reversed by the class I HDAC inhibitor mocetinostat.
Meidhof, S; Brabletz, S; Lehmann, W; Preca, BT; Mock, K; Ruh, M; Schüler, J; Berthold, M; Weber, A; Burk, U; Lübbert, M; Puhr, M; Culig, Z; Wellner, U; Keck, T; Bronsert, P; Küsters, S; Hopt, UT; Stemmler, MP; Brabletz, T
EMBO molecular medicine
7
831-47
2015
Show Abstract
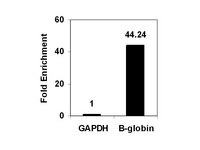
Therapy resistance is a major clinical problem in cancer medicine and crucial for disease relapse and progression. Therefore, the clinical need to overcome it, particularly for aggressive tumors such as pancreatic cancer, is very high. Aberrant activation of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and an associated cancer stem cell phenotype are considered a major cause of therapy resistance. Particularly, the EMT-activator ZEB1 was shown to confer stemness and resistance. We applied a systematic, stepwise strategy to interfere with ZEB1 function, aiming to overcome drug resistance. This led to the identification of both its target gene miR-203 as a major drug sensitizer and subsequently the class I HDAC inhibitor mocetinostat as epigenetic drug to interfere with ZEB1 function, restore miR-203 expression, repress stemness properties, and induce sensitivity against chemotherapy. Thereby, mocetinostat turned out to be more effective than other HDAC inhibitors, such as SAHA, indicating the relevance of the screening strategy. Our data encourage the application of mechanism-based combinations of selected epigenetic drugs with standard chemotherapy for the rational treatment of aggressive solid tumors, such as pancreatic cancer. | | | 25872941
 |
Matrix softness regulates plasticity of tumour-repopulating cells via H3K9 demethylation and Sox2 expression.
Tan, Y; Tajik, A; Chen, J; Jia, Q; Chowdhury, F; Wang, L; Chen, J; Zhang, S; Hong, Y; Yi, H; Wu, DC; Zhang, Y; Wei, F; Poh, YC; Seong, J; Singh, R; Lin, LJ; Doğanay, S; Li, Y; Jia, H; Ha, T; Wang, Y; Huang, B; Wang, N
Nature communications
5
4619
2014
Show Abstract
Tumour-repopulating cells (TRCs) are a self-renewing, tumorigenic subpopulation of cancer cells critical in cancer progression. However, the underlying mechanisms of how TRCs maintain their self-renewing capability remain elusive. Here we show that relatively undifferentiated melanoma TRCs exhibit plasticity in Cdc42-mediated mechanical stiffening, histone 3 lysine residue 9 (H3K9) methylation, Sox2 expression and self-renewal capability. In contrast to differentiated melanoma cells, TRCs have a low level of H3K9 methylation that is unresponsive to matrix stiffness or applied forces. Silencing H3K9 methyltransferase G9a or SUV39h1 elevates the self-renewal capability of differentiated melanoma cells in a Sox2-dependent manner. Mechanistically, H3K9 methylation at the Sox2 promoter region inhibits Sox2 expression that is essential in maintaining self-renewal and tumorigenicity of TRCs both in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our data suggest that 3D soft-fibrin-matrix-mediated cell softening, H3K9 demethylation and Sox2 gene expression are essential in regulating TRC self-renewal. | Western Blotting | Mouse | 25099074
 |
Nuclear actin filaments recruit cofilin and actin-related protein 3, and their formation is connected with a mitotic block.
Kalendová, A; Kalasová, I; Yamazaki, S; Uličná, L; Harata, M; Hozák, P
Histochemistry and cell biology
142
139-52
2014
Show Abstract
Although actin monomers polymerize into filaments in the cytoplasm, the form of actin in the nucleus remains elusive. We searched for the form and function of β-actin fused to nuclear localization signal and to enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EN-actin). Our results reveal that EN-actin is either dispersed in the nucleoplasm (homogenous EN-actin) or forms bundled filaments in the nucleus (EN-actin filaments). Formation of such filaments was not connected with increased EN-actin levels. Among numerous actin-binding proteins tested, only cofilin is recruited to the EN-actin filaments. Overexpression of EN-actin causes increase in the nuclear levels of actin-related protein 3 (Arp3). Although Arp3, a member of actin nucleation complex Arp2/3, is responsible for EN-actin filament nucleation and bundling, the way cofilin affects nuclear EN-actin filaments dynamics is not clear. While cells with homogenous EN-actin maintained unaffected mitosis during which EN-actin re-localizes to the plasma membrane, generation of nuclear EN-actin filaments severely decreases cell proliferation and interferes with mitotic progress. The introduction of EN-actin manifests in two mitotic-inborn defects-formation of binucleic cells and generation of micronuclei-suggesting that cells suffer aberrant cytokinesis and/or impaired chromosomal segregation. In interphase, nuclear EN-actin filaments passed through chromatin region, but do not co-localize with either chromatin remodeling complexes or RNA polymerases I and II. Surprisingly presence of EN-actin filaments was connected with increase in the overall transcription levels in the S-phase by yet unknown mechanism. Taken together, EN-actin can form filaments in the nucleus which affect important cellular processes such as transcription and mitosis. | | | 25002125
 |
Histone H3K9 methyltransferase G9a represses PPARγ expression and adipogenesis.
Wang, L; Xu, S; Lee, JE; Baldridge, A; Grullon, S; Peng, W; Ge, K
The EMBO journal
32
45-59
2013
Show Abstract
PPARγ promotes adipogenesis while Wnt proteins inhibit adipogenesis. However, the mechanisms that control expression of these positive and negative master regulators of adipogenesis remain incompletely understood. By genome-wide histone methylation profiling in preadipocytes, we find that among gene loci encoding adipogenesis regulators, histone methyltransferase (HMT) G9a-mediated repressive epigenetic mark H3K9me2 is selectively enriched on the entire PPARγ locus. H3K9me2 and G9a levels decrease during adipogenesis, which correlates inversely with induction of PPARγ. Removal of H3K9me2 by G9a deletion enhances chromatin opening and binding of the early adipogenic transcription factor C/EBPβ to PPARγ promoter, which promotes PPARγ expression. Interestingly, G9a represses PPARγ expression in an HMT activity-dependent manner but facilitates Wnt10a expression independent of its enzymatic activity. Consistently, deletion of G9a or inhibiting G9a HMT activity promotes adipogenesis. Finally, deletion of G9a in mouse adipose tissues increases adipogenic gene expression and tissue weight. Thus, by inhibiting PPARγ expression and facilitating Wnt10a expression, G9a represses adipogenesis. | Western Blotting | | 23178591
 |
Expression and epigenetic regulation of angiogenesis-related factors during dormancy and recurrent growth of ovarian carcinoma.
Lyu, T; Jia, N; Wang, J; Yan, X; Yu, Y; Lu, Z; Bast, RC; Hua, K; Feng, W
Epigenetics
8
1330-46
2013
Show Abstract
The initiation of angiogenesis can mark the transition from tumor dormancy to active growth and recurrence. Mechanisms that regulate recurrence in human cancers are poorly understood, in part because of the absence of relevant models. The induction of ARHI (DIRAS3) induces dormancy and autophagy in human ovarian cancer xenografts but produces autophagic cell death in culture. The addition of VEGF to cultures maintains the viability of dormant autophagic cancer cells, thereby permitting active growth when ARHI is downregulated, which mimics the "recurrence" of growth in xenografts. Two inducible ovarian cancer cell lines, SKOv3-ARHI and Hey-ARHI, were used. The expression level of angiogenesis factors was evaluated by real-time PCR, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry and western blot; their epigenetic regulation was measured by bisulfite sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation. Six of the 15 angiogenesis factors were upregulated in dormant cancer cells (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3, TIMP3; thrombospondin-1, TSP1; angiopoietin-1; angiopoietin-2; angiopoietin-4; E-cadherin, CDH1). We found that TIMP3 and CDH1 expression was regulated epigenetically and was related inversely to the DNA methylation of their promoters in cell cultures and in xenografts. Increased H3K9 acetylation was associated with higher TIMP3 expression in dormant SKOv3-ARHI cells, while decreased H3K27me3 resulted in the upregulation of TIMP3 in dormant Hey-ARHI cells. Elevated CDH1 expression during dormancy was associated with an increase in both H3K4me3 and H3K9Ac in two cell lines. CpG demethylating agents and/or histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibited the re-growth of dormant cancer cells, which was associated with the re-expression of anti-angiogenic genes. The expression of the anti-angiogenic genes TIMP3 and CDH1 is elevated during dormancy and is reduced during the transition to active growth by changes in DNA methylation and histone modification. | | | 24135786
 |
The histone H3 methyltransferase G9A epigenetically activates the serine-glycine synthesis pathway to sustain cancer cell survival and proliferation.
Ding, J; Li, T; Wang, X; Zhao, E; Choi, JH; Yang, L; Zha, Y; Dong, Z; Huang, S; Asara, JM; Cui, H; Ding, HF
Cell metabolism
18
896-907
2013
Show Abstract
Increased activation of the serine-glycine biosynthetic pathway is an integral part of cancer metabolism that drives macromolecule synthesis needed for cell proliferation. Whether this pathway is under epigenetic control is unknown. Here we show that the histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methyltransferase G9A is required for maintaining the pathway enzyme genes in an active state marked by H3K9 monomethylation and for the transcriptional activation of this pathway in response to serine deprivation. G9A inactivation depletes serine and its downstream metabolites, triggering cell death with autophagy in cancer cell lines of different tissue origins. Higher G9A expression, which is observed in various cancers and is associated with greater mortality in cancer patients, increases serine production and enhances the proliferation and tumorigenicity of cancer cells. These findings identify a G9A-dependent epigenetic program in the control of cancer metabolism, providing a rationale for G9A inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. | | | 24315373
 |
5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine reactivates gene expression via degradation of pRb pocket proteins.
Zheng, Z; Li, L; Liu, X; Wang, D; Tu, B; Wang, L; Wang, H; Zhu, WG
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology
26
449-59
2012
Show Abstract
Not only does 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-aza-CdR) induce the reexpression of silenced genes through the demethylation of CpG islands, but it increases the expression of unmethylated genes. However, the mechanism by which 5-aza-CdR activates the expression of genes is not completely understood. Here, we report that the pRb pocket proteins pRb, p107, and p130 were degraded in various cancer cell lines in response to 5-aza-CdR treatment, and this effect was dependent on the proteasome pathway. Mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) played a critical role in this 5-aza-CdR-induced degradation of pRb. Furthermore, PP2A phosphatase-induced MDM2 dephosphorylation at S260 was found to be essential for MDM2 binding to pRb in the presence of 5-aza-CdR. pRb degradation resulted in the significant reexpression of several genes, including methylated CDKN2A, RASFF1A, and unmethylated CDKN2D. Finally, knockdown of pRb pocket proteins by either RNAi or 5-aza-CdR treatment induced a significant decrease in the recruitment of SUV39H1 and an increase in the enrichment of KDM3B and KDM4A to histones around the promoter of RASFF1A and thus reduced H3K9 di- and trimethylation, by which RASFF1A expression is activated. Our data reveal a novel mechanism by which 5-aza-CdR induces the expression of both methylated and unmethylated genes by degrading pRb pocket proteins. | | | 21990374
 |
Zinc-induced Dnmt1 expression involves antagonism between MTF-1 and nuclear receptor SHP.
Zhang, Y; Andrews, GK; Wang, L
Nucleic acids research
40
4850-60
2012
Show Abstract
Dnmt1 is frequently overexpressed in cancers, which contributes significantly to cancer-associated epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes. However, the mechanism of Dnmt1 overexpression remains elusive. Herein, we elucidate a pathway through which nuclear receptor SHP inhibits zinc-dependent induction of Dnmt1 by antagonizing metal-responsive transcription factor-1 (MTF-1). Zinc treatment induces Dnmt1 transcription by increasing the occupancy of MTF-1 on the Dnmt1 promoter while decreasing SHP expression. SHP in turn represses MTF-1 expression and abolishes zinc-mediated changes in the chromatin configuration of the Dnmt1 promoter. Dnmt1 expression is increased in SHP-knockout (sko) mice but decreased in SHP-transgenic (stg) mice. In human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), increased DNMT1 expression is negatively correlated with SHP levels. Our study provides a molecular explanation for increased Dnmt1 expression in HCC and highlights SHP as a potential therapeutic target. | | | 22362755
 |
Plant 45S rDNA clusters are fragile sites and their instability is associated with epigenetic alterations.
Huang, M; Li, H; Zhang, L; Gao, F; Wang, P; Hu, Y; Yan, S; Zhao, L; Zhang, Q; Tan, J; Liu, X; He, S; Li, L
PloS one
7
e35139
2012
Show Abstract
Our previous study demonstrated that 45S ribosomal DNA (45S rDNA) clusters were chromosome fragile sites expressed spontaneously in Lolium. In this study, fragile phenotypes of 45S rDNA were observed under aphidicolin (APH) incubation in several plant species. Further actinomycin D (ActD) treatment showed that transcriptional stress might interfere with chromatin packaging, resulting in 45S rDNA fragile expression. These data identified 45S rDNA sites as replication-dependent as well as transcription-dependent fragile sites in plants. In the presence of ActD, a dramatic switch to an open chromatin conformation and accumulated incomplete 5' end of the external transcribed spacer (5'ETS) transcripts were observed, accompanied by decreased DNA methylation, decreased levels of histone H3, and increased histone acetylation and levels of H3K4me2, suggesting that these epigenetic alterations are associated with failure of 45S rDNA condensation. Furthermore, the finding that γ-H2AX was accumulated at 45S rDNA sites following ActD treatment suggested that the DNA damage signaling pathway was associated with the appearance of 45S rDNA fragile phenotypes. Our data provide a link between 45S rDNA transcription and chromatin-packaging defects and open the door for further identifying the molecular mechanism involved. | | | 22509394
 |
Antisilencing role of the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway and a histone acetyltransferase in Arabidopsis.
Li, X; Qian, W; Zhao, Y; Wang, C; Shen, J; Zhu, JK; Gong, Z
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
109
11425-30
2012
Show Abstract
REPRESSOR OF SILENCING 1 (ROS1) is a DNA demethylation enzyme that was previously identified during a genetic screen for the silencing of both RD29A-LUC and 35S-NPTII transgenes on a T-DNA construct. Here we performed a genetic screen to identify additional mutants in which the 35S-NPTII transgene is silenced. We identified several alleles of ros1 and of the following components of the RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) pathway: NRPD1 (the largest subunit of polymerase IV), RDR2, NRPE1 (the largest subunit of polymerase V), NRPD2, AGO4, and DMS3. Our results show that the silencing of 35S-NPTII in the RdDM pathway mutants is due to the reduced expression of ROS1 in the mutants. We also identified a putative histone acetyltransferase (ROS4) from the genetic screen. The acetyltransferase contains a PHD-finger domain that binds to unmethylated histone H3K4. The mutation in ROS4 led to reduction of H3K18 and H3K23 acetylation levels. We show that the silencing of 35S-NPTII and some transposable element genes was released by the ddm1 mutation but that this also required ROS4. Our study identifies a unique antisilencing factor, and reveals that the RdDM pathway has an antisilencing function due to its role in maintaining ROS1 expression. | Western Blotting | | 22733760
 |