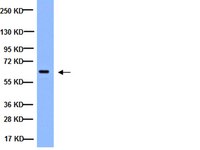
MAB3026-25UG Sigma-AldrichAnti-NFkB Antibody, p65 subunit Antibody, active subunit Antibody, clone 12H11
Use Anti-NFκB Antibody, p65 subunit, active subunit, clone 12H11 (Mouse Monoclonal Antibody) validated in EMSA, FC, ICC, IF, IHC, IHC(P), WB to detect NFκB also known as Rel A.
More>> Use Anti-NFκB Antibody, p65 subunit, active subunit, clone 12H11 (Mouse Monoclonal Antibody) validated in EMSA, FC, ICC, IF, IHC, IHC(P), WB to detect NFκB also known as Rel A. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Purified |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Purified mouse monoclonal IgG3 liquid in buffer containing 0.02 M Phosphate buffer, 0.25 M NaCl, pH 7.6 with 0.1% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 25 μg |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalog Number | GTIN |
| MAB3026-25UG | 04054839342677 |
Documentation
Anti-NFkB Antibody, p65 subunit Antibody, active subunit Antibody, clone 12H11 Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| Anti-NFkB, p65 subunit, active subunit, clone 12H11 - 3738472 | 3738472 |
| Anti-NFkB, p65 subunit, active subunit, clone 12H11 - 4011212 | 4011212 |