Minimal Change in the cytoplasmic calcium dynamics in striatal GABAergic neurons of a DYT1 dystonia knock-in mouse model.
Iwabuchi, S; Koh, JY; Wang, K; Ho, KW; Harata, NC
PloS one
8
e80793
2013
Show Abstract
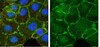
DYT1 dystonia is the most common hereditary form of primary torsion dystonia. This autosomal-dominant disorder is characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause sustained twisting and repetitive movements. It is caused by an in-frame deletion in the TOR1A gene, leading to the deletion of a glutamic acid residue in the torsinA protein. Heterozygous knock-in mice, which reproduce the genetic mutation in human patients, have abnormalities in synaptic transmission at the principal GABAergic neurons in the striatum, a brain structure that is involved in the execution and modulation of motor activity. However, whether this mutation affects the excitability of striatal GABAergic neurons has not been investigated in this animal model. Here, we examined the excitability of cultured striatal neurons obtained from heterozygous knock-in mice, using calcium imaging as indirect readout. Immunofluorescence revealed that more than 97% of these neurons are positive for a marker of GABAergic neurons, and that more than 92% are also positive for a marker of medium spiny neurons, indicating that these are mixed cultures of mostly medium spiny neurons and a few (~5%) GABAergic interneurons. When these neurons were depolarized by field stimulation, the calcium concentration in the dendrites increased rapidly and then decayed slowly. The amplitudes of calcium transients were larger in heterozygous neurons than in wild-type neurons, resulting in ~15% increase in cumulative calcium transients during a train of stimuli. However, there was no change in other parameters of calcium dynamics. Given that calcium dynamics reflect neuronal excitability, these results suggest that the mutation only slightly increases the excitability of striatal GABAergic neurons in DYT1 dystonia. | Immunocytochemistry | 24260480
 |