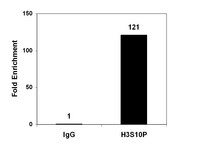
Genome-wide analysis of H4K5 acetylation associated with fear memory in mice.
Park, CS; Rehrauer, H; Mansuy, IM
BMC genomics
14
539
2013
Show Abstract
Histone acetylation has been implicated in learning and memory in the brain, however, its function at the level of the genome and at individual genetic loci remains poorly investigated. This study examines a key acetylation mark, histone H4 lysine 5 acetylation (H4K5ac), genome-wide and its role in activity-dependent gene transcription in the adult mouse hippocampus following contextual fear conditioning.Using ChIP-Seq, we identified 23,235 genes in which H4K5ac correlates with absolute gene expression in the hippocampus. However, in the absence of transcription factor binding sites 150 bp upstream of the transcription start site, genes were associated with higher H4K5ac and expression levels. We further establish H4K5ac as a ubiquitous modification across the genome. Approximately one-third of all genes have above average H4K5ac, of which ~15% are specific to memory formation and ~65% are co-acetylated for H4K12. Although H4K5ac is prevalent across the genome, enrichment of H4K5ac at specific regions in the promoter and coding region are associated with different levels of gene expression. Additionally, unbiased peak calling for genes differentially acetylated for H4K5ac identified 114 unique genes specific to fear memory, over half of which have not previously been associated with memory processes.Our data provide novel insights into potential mechanisms of gene priming and bookmarking by histone acetylation following hippocampal memory activation. Specifically, we propose that hyperacetylation of H4K5 may prime genes for rapid expression following activity. More broadly, this study strengthens the importance of histone posttranslational modifications for the differential regulation of transcriptional programs in cognitive processes. | 23927422
 |
Unliganded progesterone receptor-mediated targeting of an RNA-containing repressive complex silences a subset of hormone-inducible genes.
Vicent, GP; Nacht, AS; Zaurin, R; Font-Mateu, J; Soronellas, D; Le Dily, F; Reyes, D; Beato, M
Genes & development
27
1179-97
2013
Show Abstract
A close chromatin conformation precludes gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Genes activated by external cues have to overcome this repressive state by locally changing chromatin structure to a more open state. Although much is known about hormonal gene activation, how basal repression of regulated genes is targeted to the correct sites throughout the genome is not well understood. Here we report that in breast cancer cells, the unliganded progesterone receptor (PR) binds genomic sites and targets a repressive complex containing HP1γ (heterochromatin protein 1γ), LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1), HDAC1/2, CoREST (corepressor for REST [RE1 {neuronal repressor element 1} silencing transcription factor]), KDM5B, and the RNA SRA (steroid receptor RNA activator) to 20% of hormone-inducible genes, keeping these genes silenced prior to hormone treatment. The complex is anchored via binding of HP1γ to H3K9me3 (histone H3 tails trimethylated on Lys 9). SRA interacts with PR, HP1γ, and LSD1, and its depletion compromises the loading of the repressive complex to target chromatin-promoting aberrant gene derepression. Upon hormonal treatment, the HP1γ-LSD1 complex is displaced from these constitutively poorly expressed genes as a result of rapid phosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser 10 mediated by MSK1, which is recruited to the target sites by the activated PR. Displacement of the repressive complex enables the loading of coactivators needed for chromatin remodeling and activation of this set of genes, including genes involved in apoptosis and cell proliferation. These results highlight the importance of the unliganded PR in hormonal regulation of breast cancer cells. | 23699411
 |
Four enzymes cooperate to displace histone H1 during the first minute of hormonal gene activation.
Vicent, GP; Nacht, AS; Font-Mateu, J; Castellano, G; Gaveglia, L; Ballaré, C; Beato, M
Genes & development
25
845-62
2011
Show Abstract
Gene regulation by external signals requires access of transcription factors to DNA sequences of target genes, which is limited by the compaction of DNA in chromatin. Although we have gained insight into how core histones and their modifications influence this process, the role of linker histones remains unclear. Here we show that, within the first minute of progesterone action, a complex cooperation between different enzymes acting on chromatin mediates histone H1 displacement as a requisite for gene induction and cell proliferation. First, activated progesterone receptor (PR) recruits the chromatin remodeling complexes NURF and ASCOM (ASC-2 [activating signal cointegrator-2] complex) to hormone target genes. The trimethylation of histone H3 at Lys 4 by the MLL2/MLL3 subunits of ASCOM, enhanced by the hormone-induced displacement of the H3K4 demethylase KDM5B, stabilizes NURF binding. NURF facilitates the PR-mediated recruitment of Cdk2/CyclinA, which is required for histone H1 displacement. Cooperation of ATP-dependent remodeling, histone methylation, and kinase activation, followed by H1 displacement, is a prerequisite for the subsequent displacement of histone H2A/H2B catalyzed by PCAF and BAF. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and sequencing (ChIP-seq) and expression arrays show that H1 displacement is required for hormone induction of most hormone target genes, some of which are involved in cell proliferation. | 21447625
 |