36-008-25UL Sigma-AldrichAnti-a-Synuclein clone Syn211
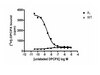
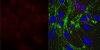
Detect α-Synuclein using this Anti-α-Synuclein Antibody, clone Syn211 validated for use in IP, WB, IH.
More>> Detect α-Synuclein using this Anti-α-Synuclein Antibody, clone Syn211 validated for use in IP, WB, IH. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Specifications Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | IP, WB, IHC | M | Ascites | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | 36-008-25UL |
| Brand Family | Upstate |
| Trade Name |
|
| Description | Anti-a-Synuclein clone Syn211 |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Ascites |
| Presentation | Ascites |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Applications | |
|---|---|
| Application | Detect α-Synuclein using this Anti-α-Synuclein Antibody, clone Syn211 validated for use in IP, WB, IH. |
| Key Applications |
|
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | 2 years at -20°C |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 25 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalog Number | GTIN |
| 36-008-25UL | 04054839337352 |
Documentation
Anti-a-Synuclein clone Syn211 SDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-a-Synuclein clone Syn211 Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| Anti-α-Synuclein, clone Syn211 (mouse ascites) | 2987655 |
| Anti-α-Synuclein, clone Syn211 - 3425410 | 3425410 |
| Anti-α-Synuclein, clone Syn211 - 4139158 | 4139158 |