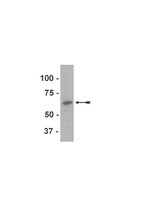
Gfi1 expressed in bone marrow stromal cells is a novel osteoblast suppressor in patients with multiple myeloma bone disease.
D'Souza, S; del Prete, D; Jin, S; Sun, Q; Huston, AJ; Kostov, FE; Sammut, B; Hong, CS; Anderson, JL; Patrene, KD; Yu, S; Velu, CS; Xiao, G; Grimes, HL; Roodman, GD; Galson, DL
Blood
118
6871-80
2011
Show Abstract
Protracted inhibition of osteoblast (OB) differentiation characterizes multiple myeloma (MM) bone disease and persists even when patients are in long-term remission. However, the underlying pathophysiology for this prolonged OB suppression is unknown. Therefore, we developed a mouse MM model in which the bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) remained unresponsive to OB differentiation signals after removal of MM cells. We found that BMSCs from both MM-bearing mice and MM patients had increased levels of the transcriptional repressor Gfi1 compared with controls and that Gfi1 was a novel transcriptional repressor of the critical OB transcription factor Runx2. Trichostatin-A blocked the effects of Gfi1, suggesting that it induces epigenetic changes in the Runx2 promoter. MM-BMSC cell-cell contact was not required for MM cells to increase Gfi1 and repress Runx2 levels in MC-4 before OBs or naive primary BMSCs, and Gfi1 induction was blocked by anti-TNF-α and anti-IL-7 antibodies. Importantly, BMSCs isolated from Gfi1(-/-) mice were significantly resistant to MM-induced OB suppression. Strikingly, siRNA knockdown of Gfi1 in BMSCs from MM patients significantly restored expression of Runx2 and OB differentiation markers. Thus, Gfi1 may have an important role in prolonged MM-induced OB suppression and provide a new therapeutic target for MM bone disease. | | 22042697
 |
Growth factor independence-1 is expressed in primary human neuroendocrine lung carcinomas and mediates the differentiation of murine pulmonary neuroendocrine cells.
Kazanjian, Avedis, et al.
Cancer Res., 64: 6874-82 (2004)
2004
Show Abstract
Human small cell lung cancers might be derived from pulmonary cells with a neuroendocrine phenotype. They are driven to proliferate by autocrine and paracrine neuropeptide growth factor stimulation. The molecular basis of the neuroendocrine phenotype of lung carcinomas is relatively unknown. The Achaete-Scute Homologue-1 (ASH1) transcription factor is critically required for the formation of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and is a marker for human small cell lung cancers. The Drosophila orthologues of ASH1 (Achaete and Scute) and the growth factor independence-1 (GFI1) oncoprotein (Senseless) genetically interact to inhibit Notch signaling and specify fly sensory organ development. Here, we show that GFI1, as with ASH1, is expressed in neuroendocrine lung cancer cell lines and that GFI1 in lung cancer cell lines functions as a DNA-binding transcriptional repressor protein. Forced expression of GFI1 potentiates tumor formation of small-cell lung carcinoma cells. In primary human lung cancer specimens, GFI1 expression strongly correlates with expression of ASH1, the neuroendocrine growth factor gastrin-releasing peptide, and neuroendocrine markers synaptophysin and chromogranin A (P < 0.0000001). GFI1 colocalizes with chromogranin A and calcitonin-gene-related peptide in embryonic and adult murine pulmonary neuroendocrine cells. In addition, mice with a mutation in GFI1 display abnormal development of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, indicating that GFI1 is important for neuroendocrine differentiation. | Immunohistochemistry (Tissue) | 15466176
 |